Should the government intervene in the economy?
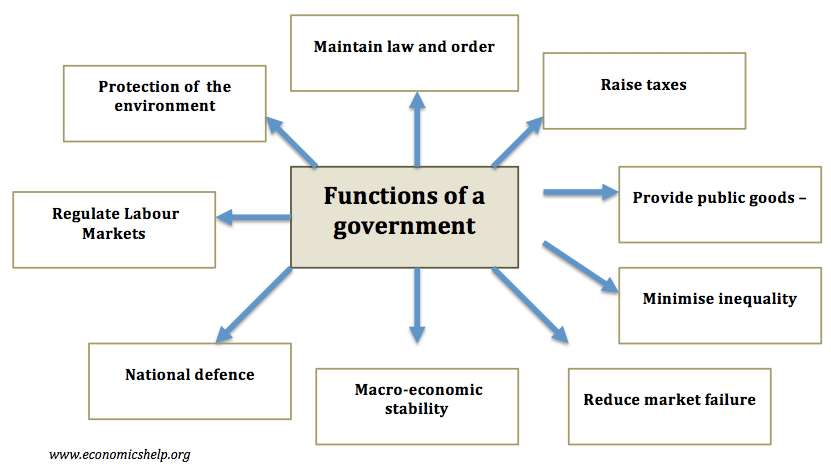
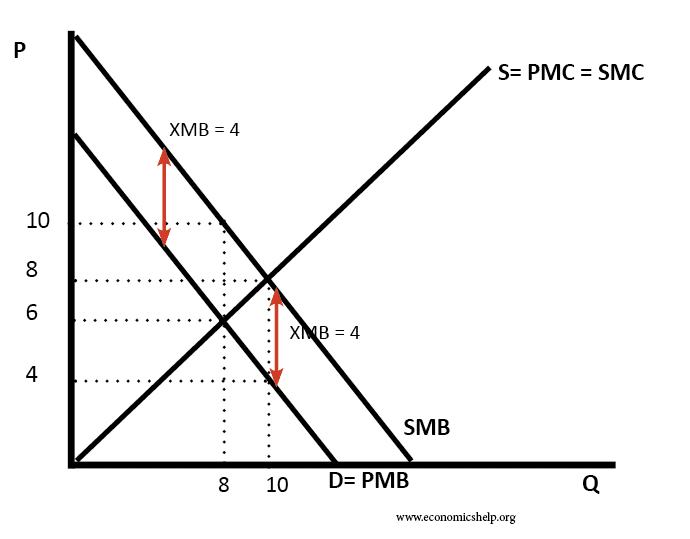
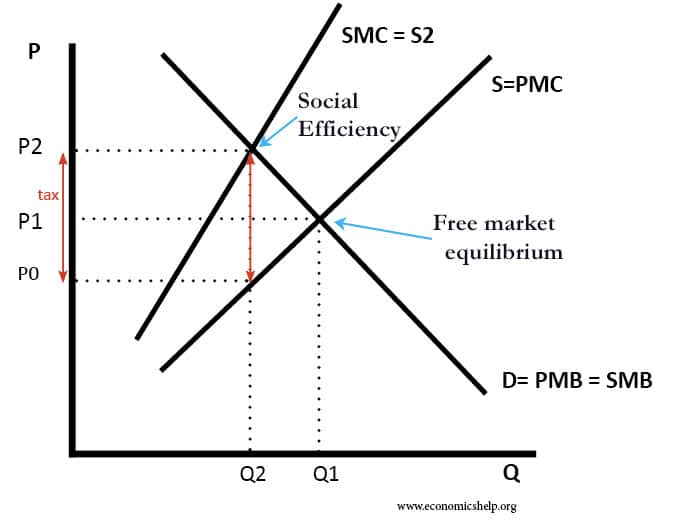
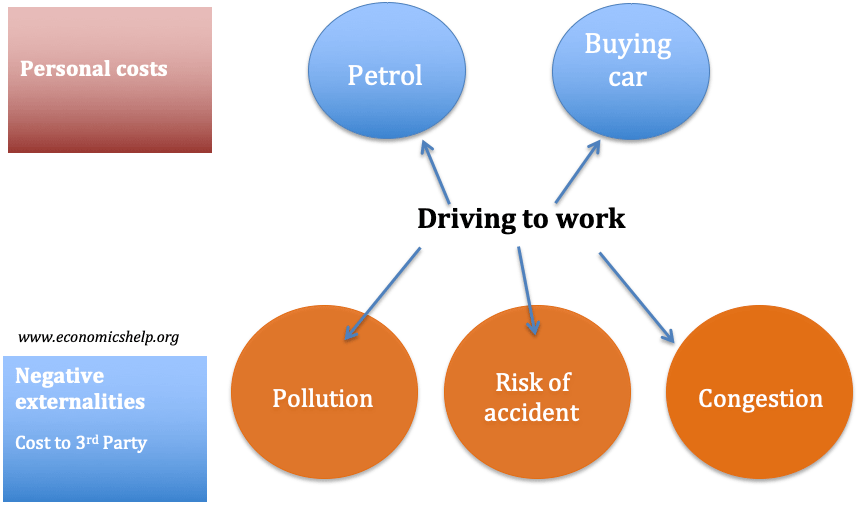
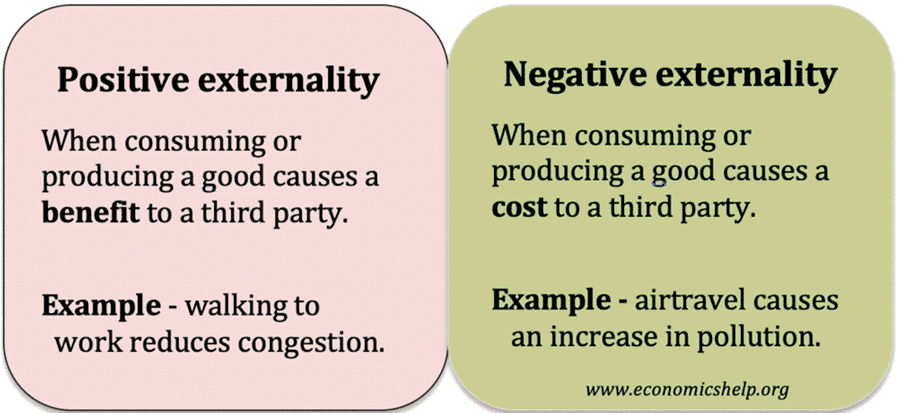
One of the main issues in economics is the extent to which the government should intervene in the economy. Free market economists argue that government intervention should be strictly limited as government intervention tends to cause an inefficient allocation of resources. However, others argue there is a strong case for government intervention in different fields, …