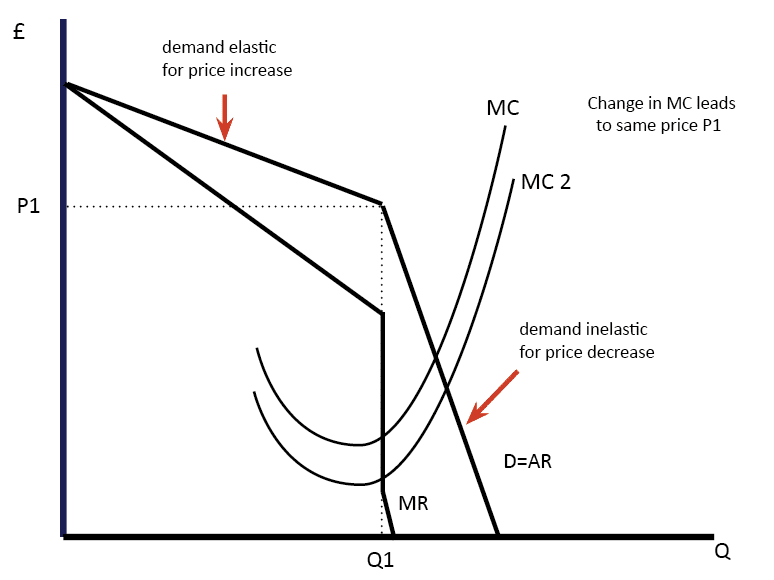
Kinked demand curve
A kinked demand curve occurs when the demand curve is not a straight line but has a different elasticity for higher and lower prices. One example of a kinked demand curve is the model for an oligopoly. This model of oligopoly suggests that prices are rigid and that firms will face different effects for both …