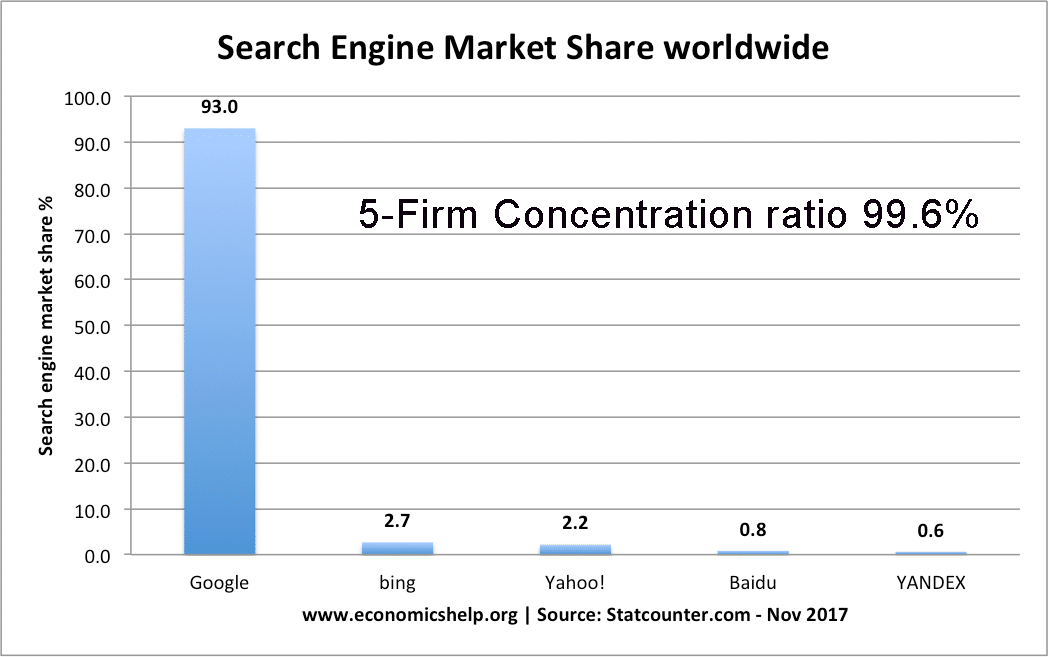
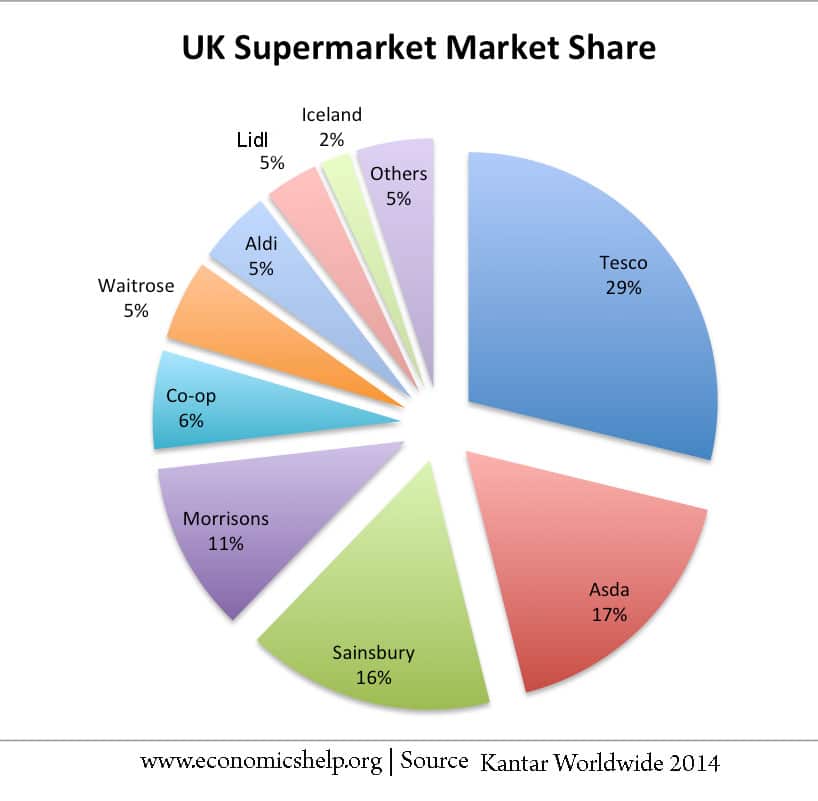
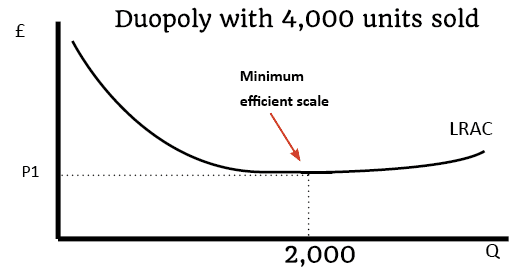
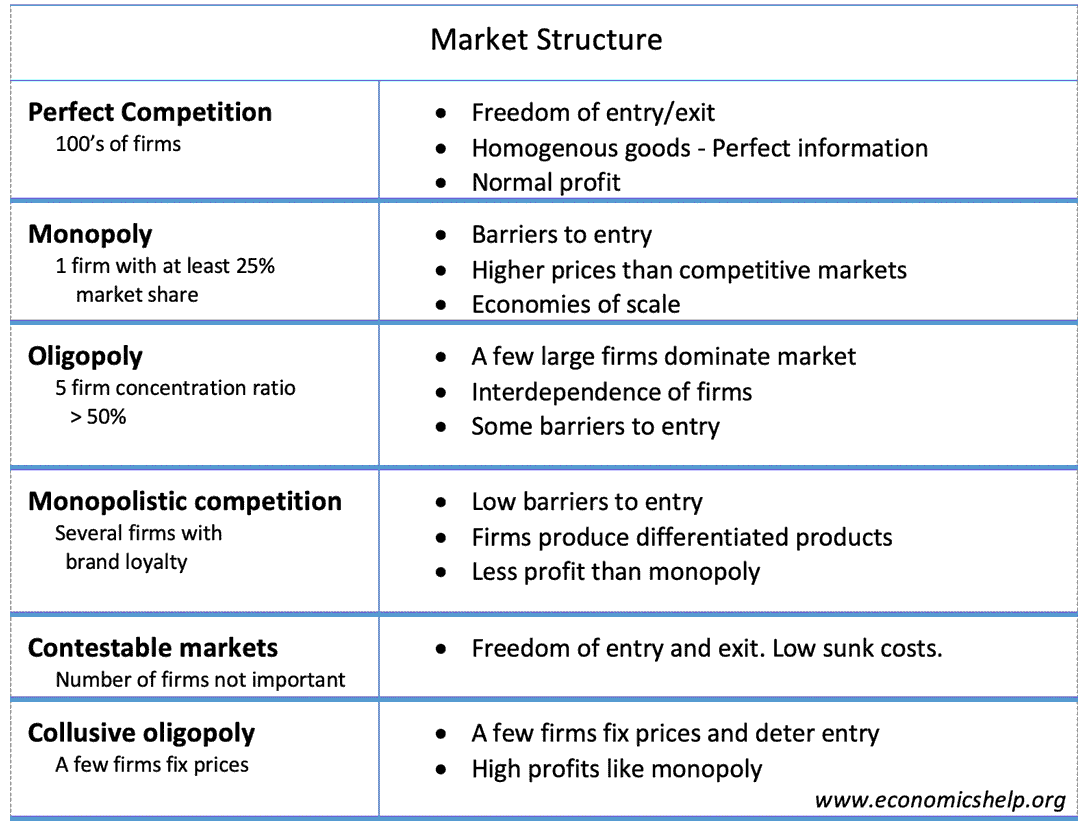
Concentration Ratios
Definition of Concentration Ratios The percentage of market share taken up by the largest firms. It could be a 3 firm concentration ratio (market share of 3 biggest) or a 5 firm concentration ratio. Concentration ratios are used to determine the market structure and competitiveness of the market. For example, an oligopoly is defined when …