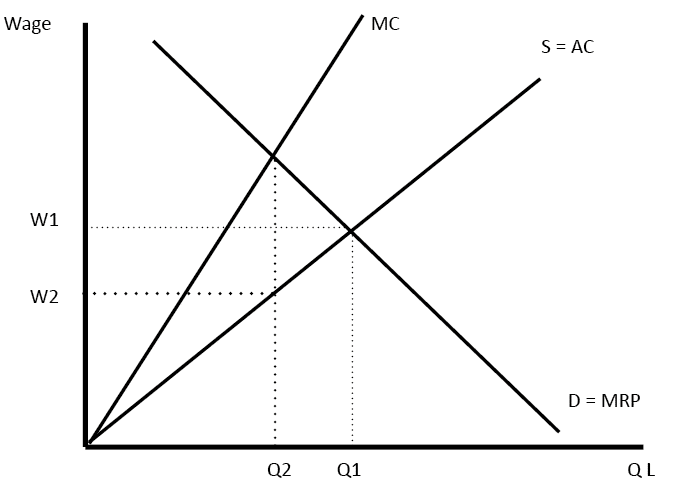
Effect of US steel tariffs
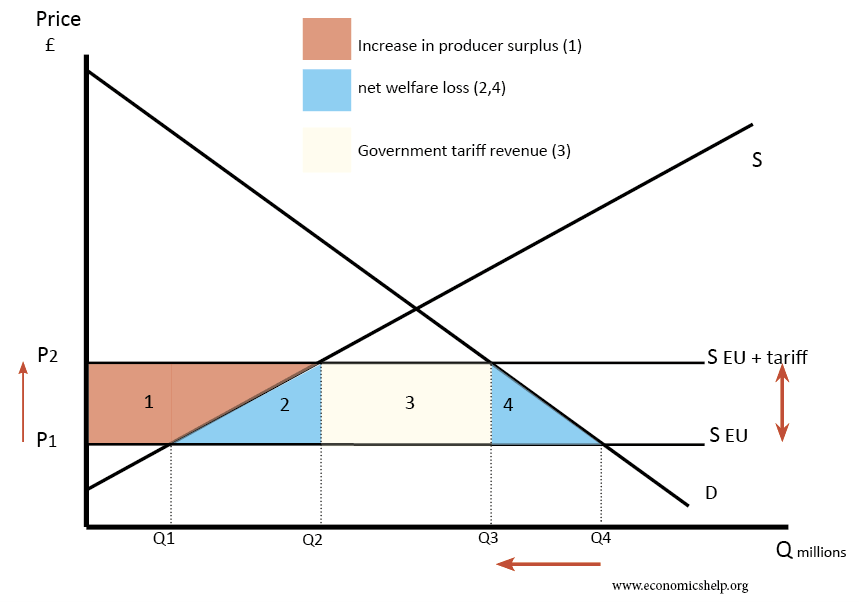
What would be the impact of the US placing a tariff on the import of steel and aluminium into the US A tariff on imports of foreign steel would raise the price of imported steel and encourage US firms and consumers to buy domestically produced steel instead. At the moment, American producers find it cheaper …