Economic objectives of firms
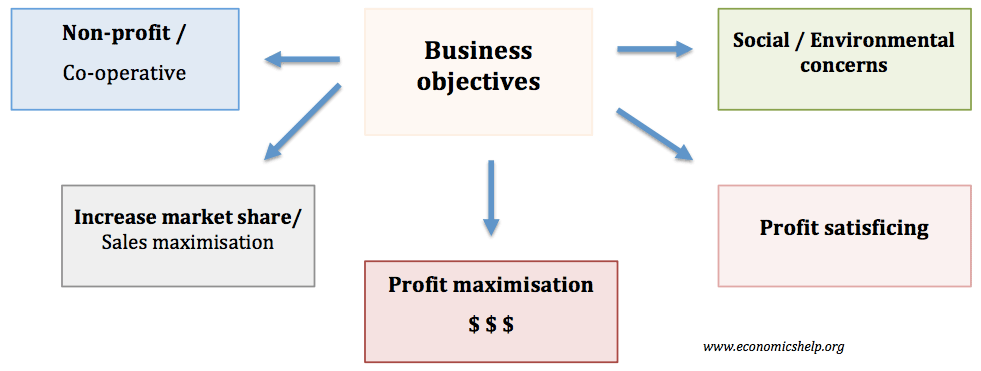
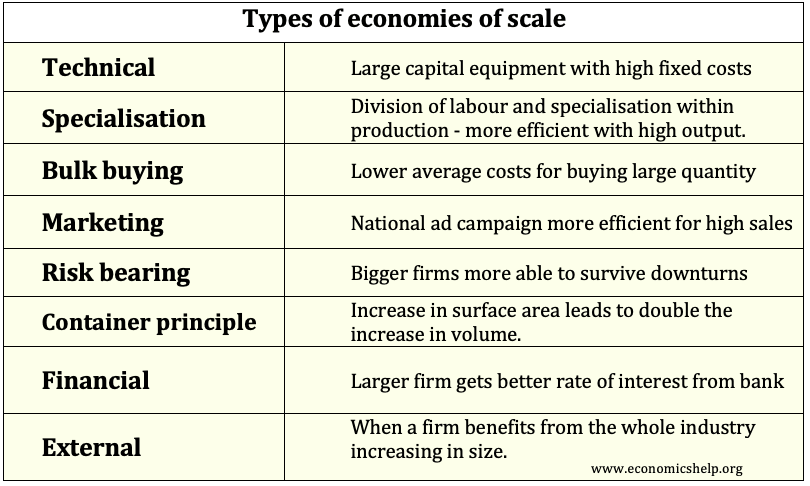
The main objectives of firms are: Profit maximisation Sales maximisation Increased market share/market dominance Social/environmental concerns Profit satisficing Co-operatives Business Objectives of firmsWatch this video on YouTube Sometimes there is an overlap of objectives. For example, seeking to increase market share, may lead to lower profits in the short-term, but enable profit maximisation in the …