Market Failure
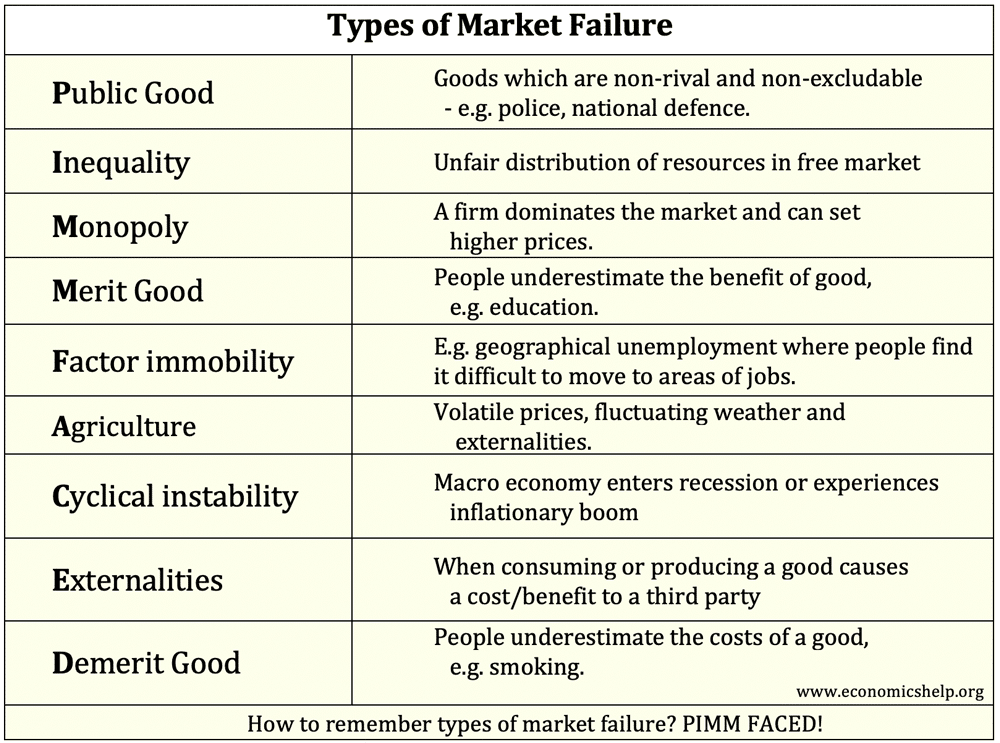
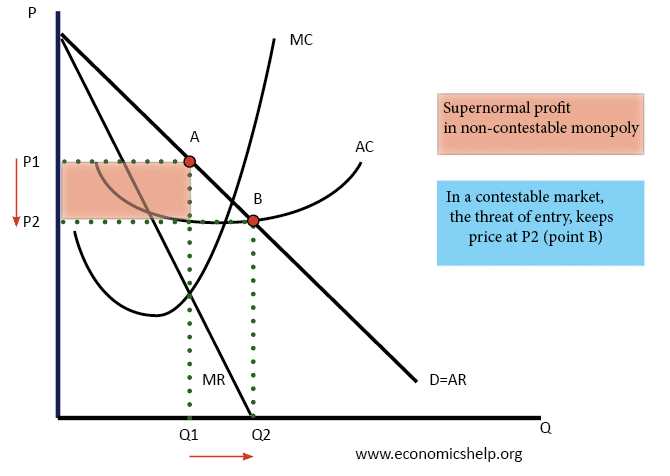
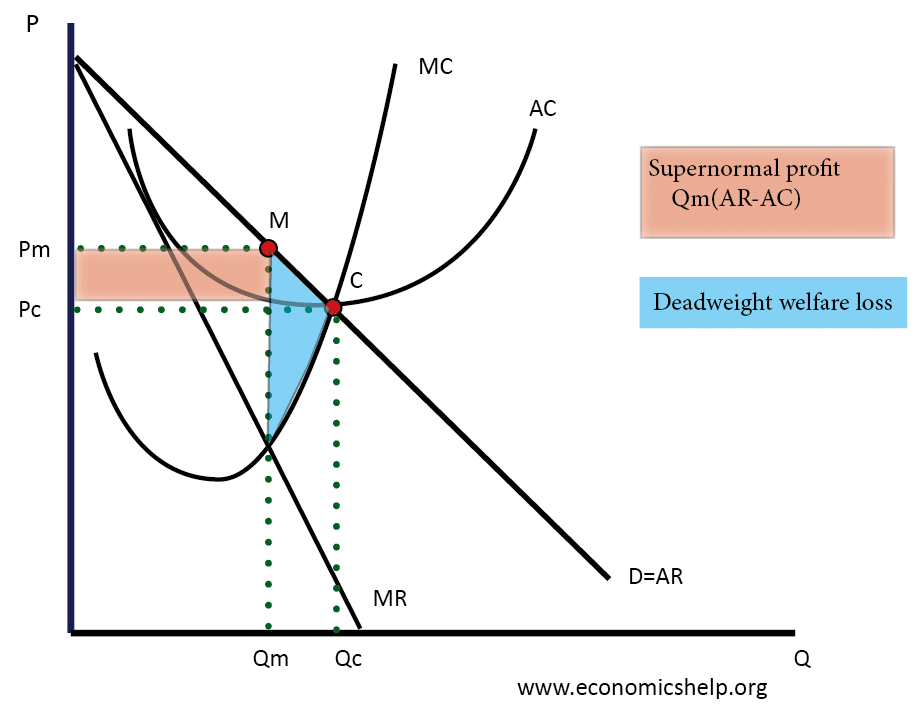
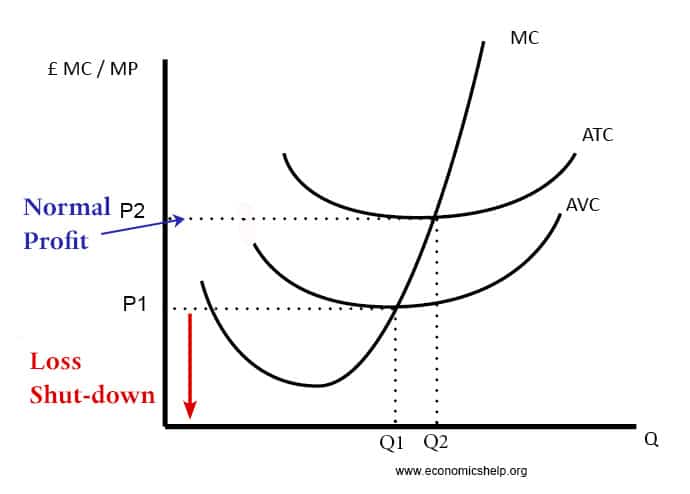
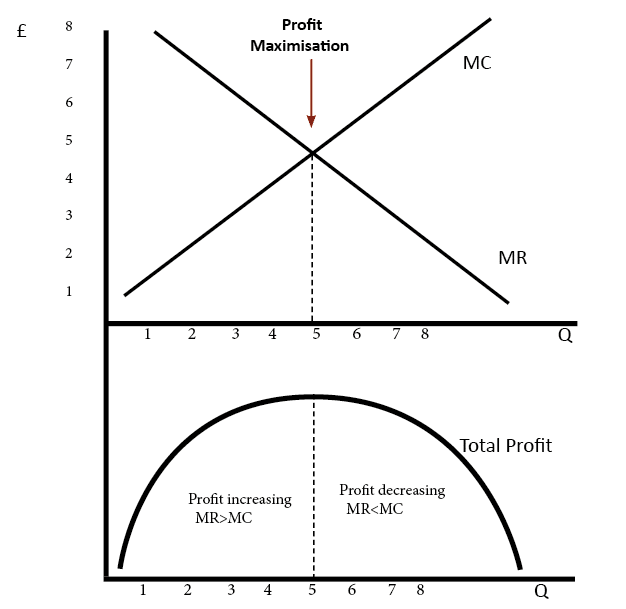
Definition of Market Failure – This occurs when there is an inefficient allocation of resources in a free market. Market failure can occur due to a variety of reasons, such as monopoly (higher prices and less output), negative externalities (over-consumed and costs to third party) and public goods (usually not provided in a free market) …