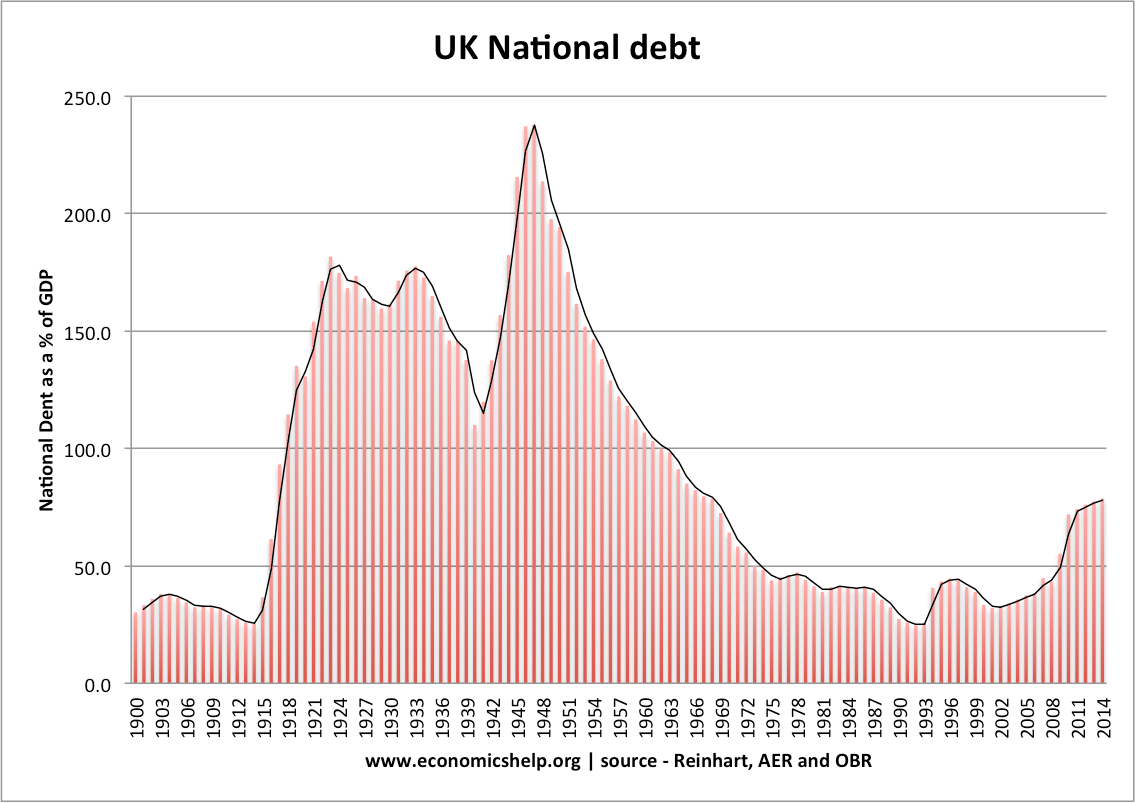
Quantitative Easing Definition
Definition Quantitative Easing. This involves the Central Bank increasing the money supply and using these electronically created funds to buy government bonds or other securities. Quantitative easing is a form of expansionary monetary policy. It is usually used in a liquidity trap – when base interest rates cannot be cut any further. Aim of Quantitative …