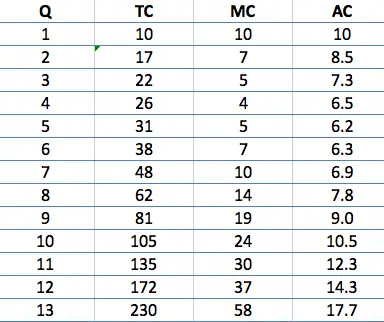
Sunk costs
A sunk cost is an irretrievable cost. Once spent, the sunk cost cannot be recovered when the firm leaves the industry. A sunk cost is incurred in the past and cannot be changed. A non-sunk cost is a cost that will only occur if a particular decision is made. Examples of sunk costs Advertising expenditure. …