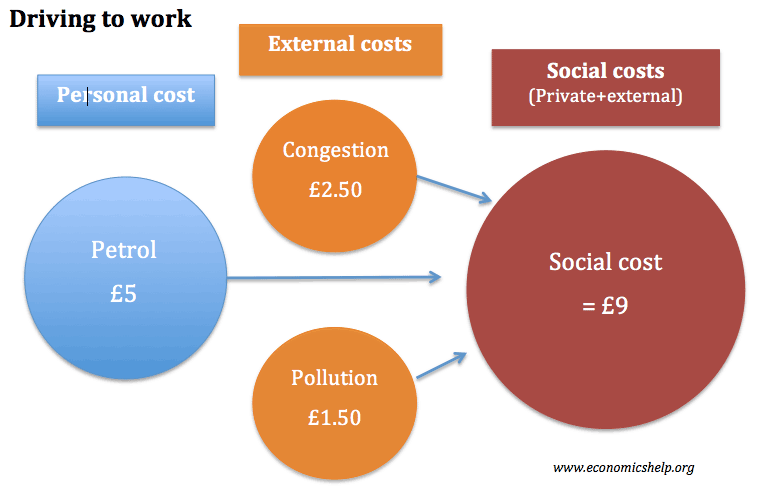
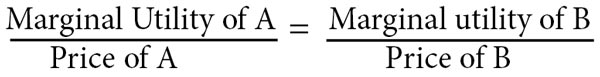How immigration benefits and imposes costs on an economy
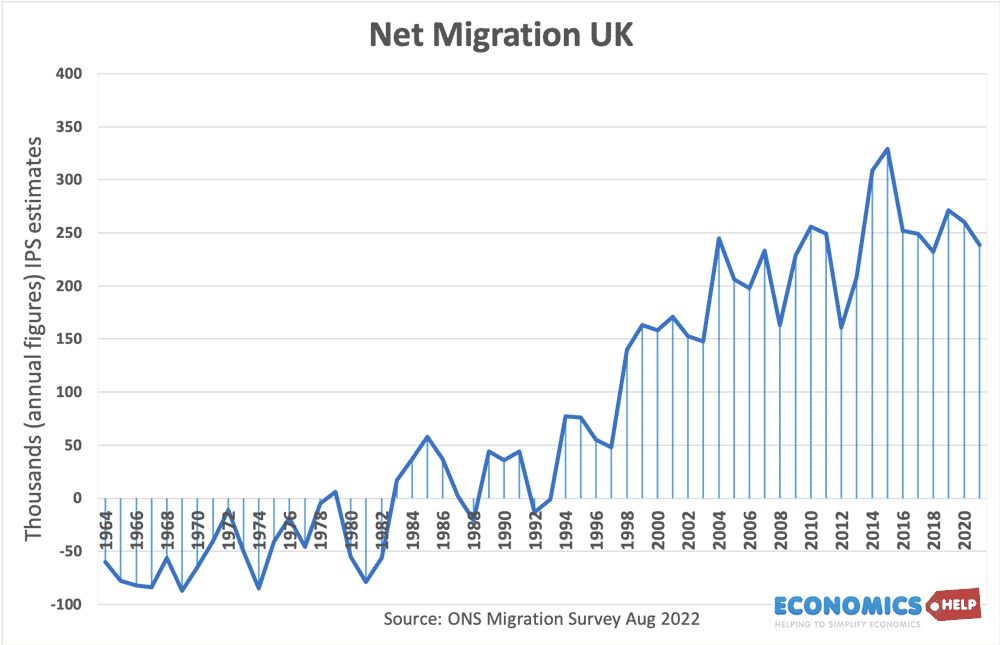
On a basic level net migration will increase gross domestic product, for two reasons. Bigger workforce Increase in demand in the economy. But what effect will immigration have on per capita income, tax revenues employment and other factors affecting living standards like housing costs? The Economic Costs and Benefits of Immigration – The Surprising Winners …