Phillips Curve Explained
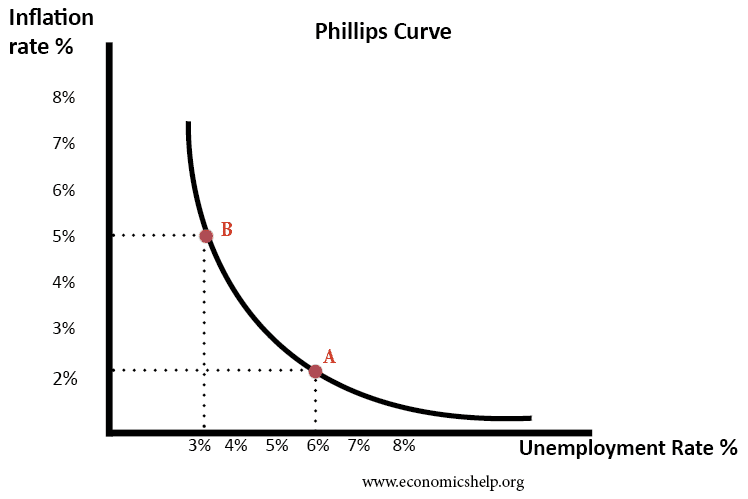
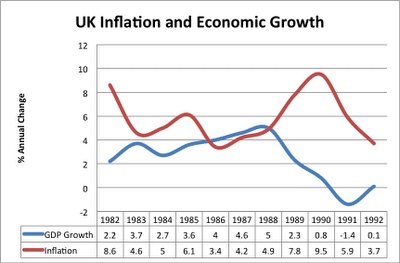
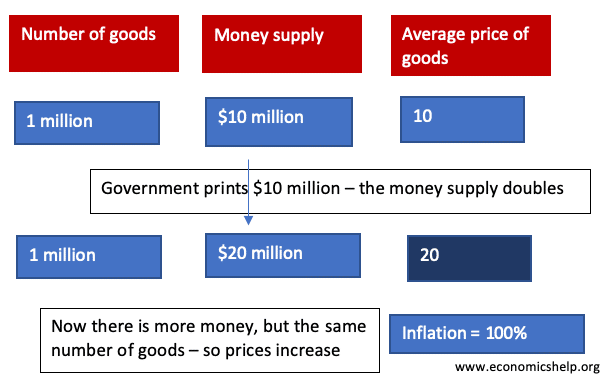
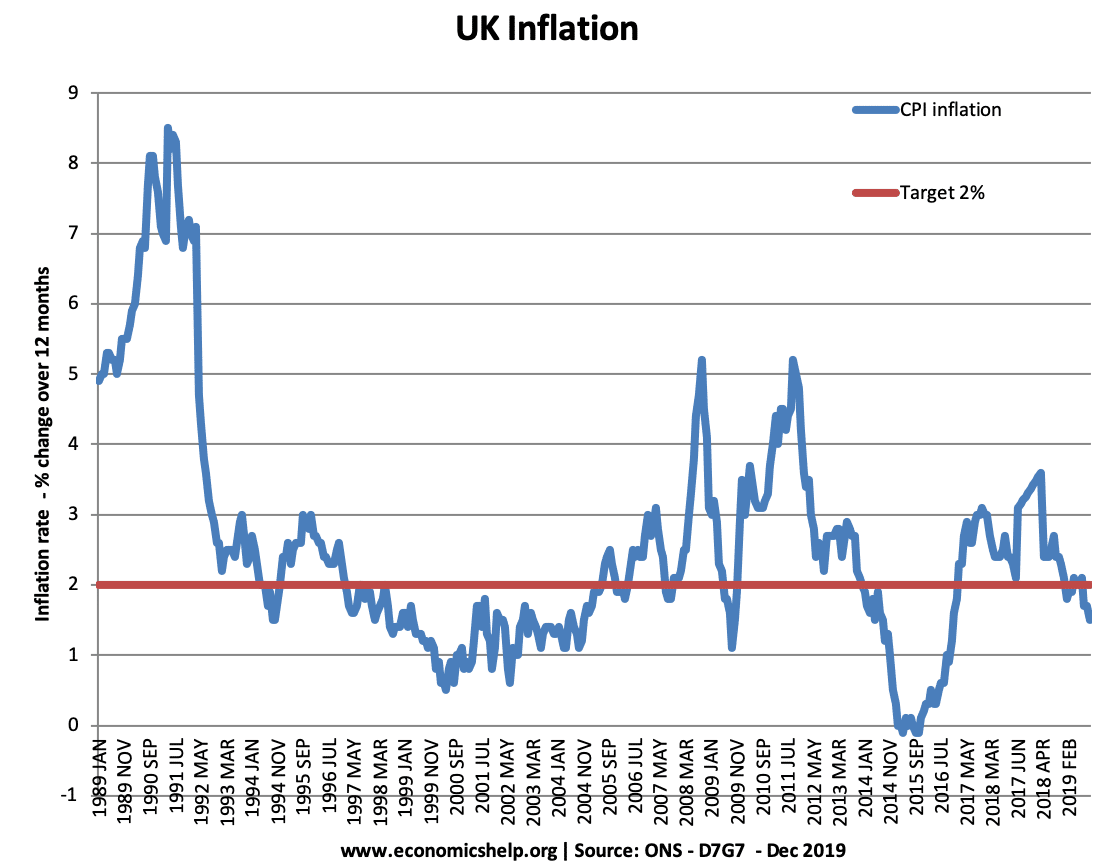
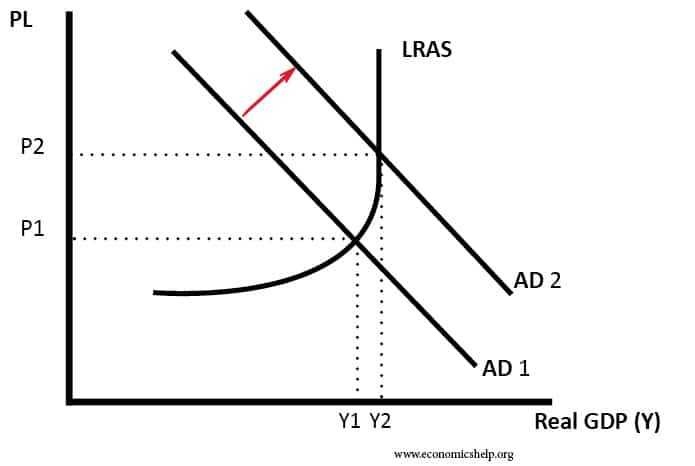
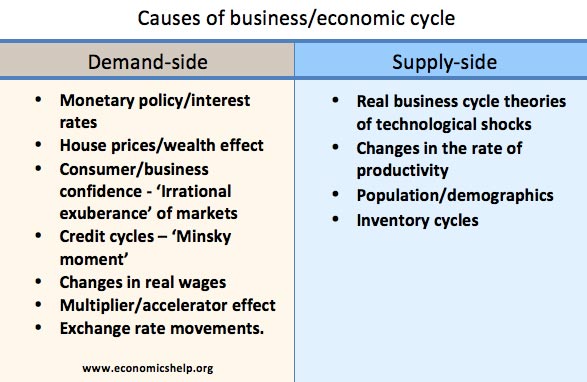
Summary of Phillips Curve The Phillips curve suggests there is an inverse relationship between inflation and unemployment. This suggests policymakers have a choice between prioritising inflation or unemployment. During the 1950s and 1960s, Phillips curve analysis suggested there was a trade-off, and policymakers could use demand management (fiscal and monetary policy) to try and influence …