Trade Liberalisation
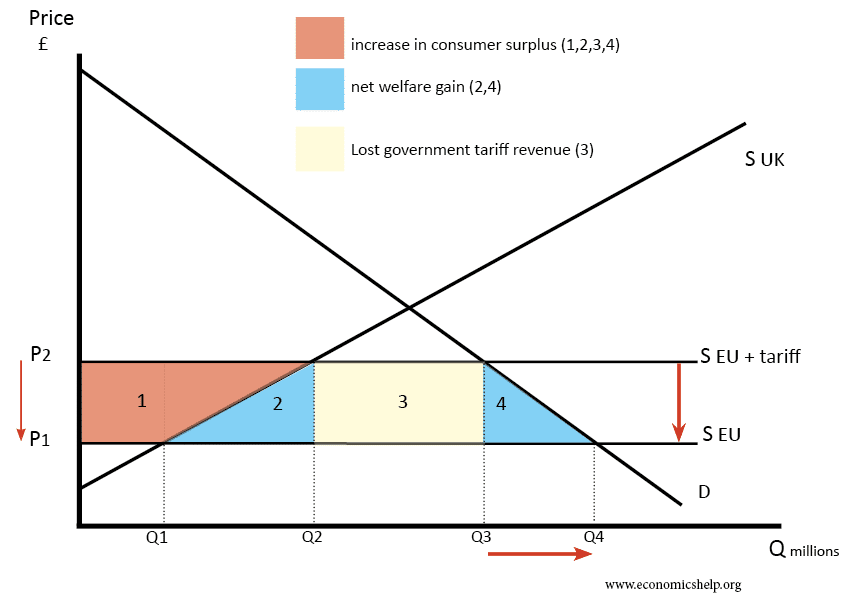
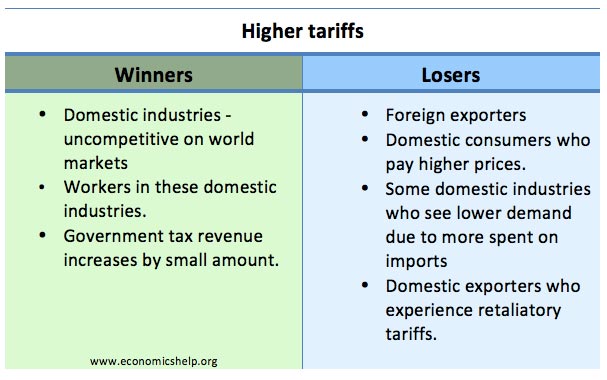
Definition Trade liberalisation involves removing barriers to trade between different countries and encouraging free trade. Trade liberalisation involves: Reducing tariffs Reducing/eliminating quotas Reducing non-tariff barriers. Non-tariff barriers are factors that make trade difficult and expensive. For example, having specific regulations on making goods can give an unfair advantage to domestic producers. Harmonising environmental and safety …