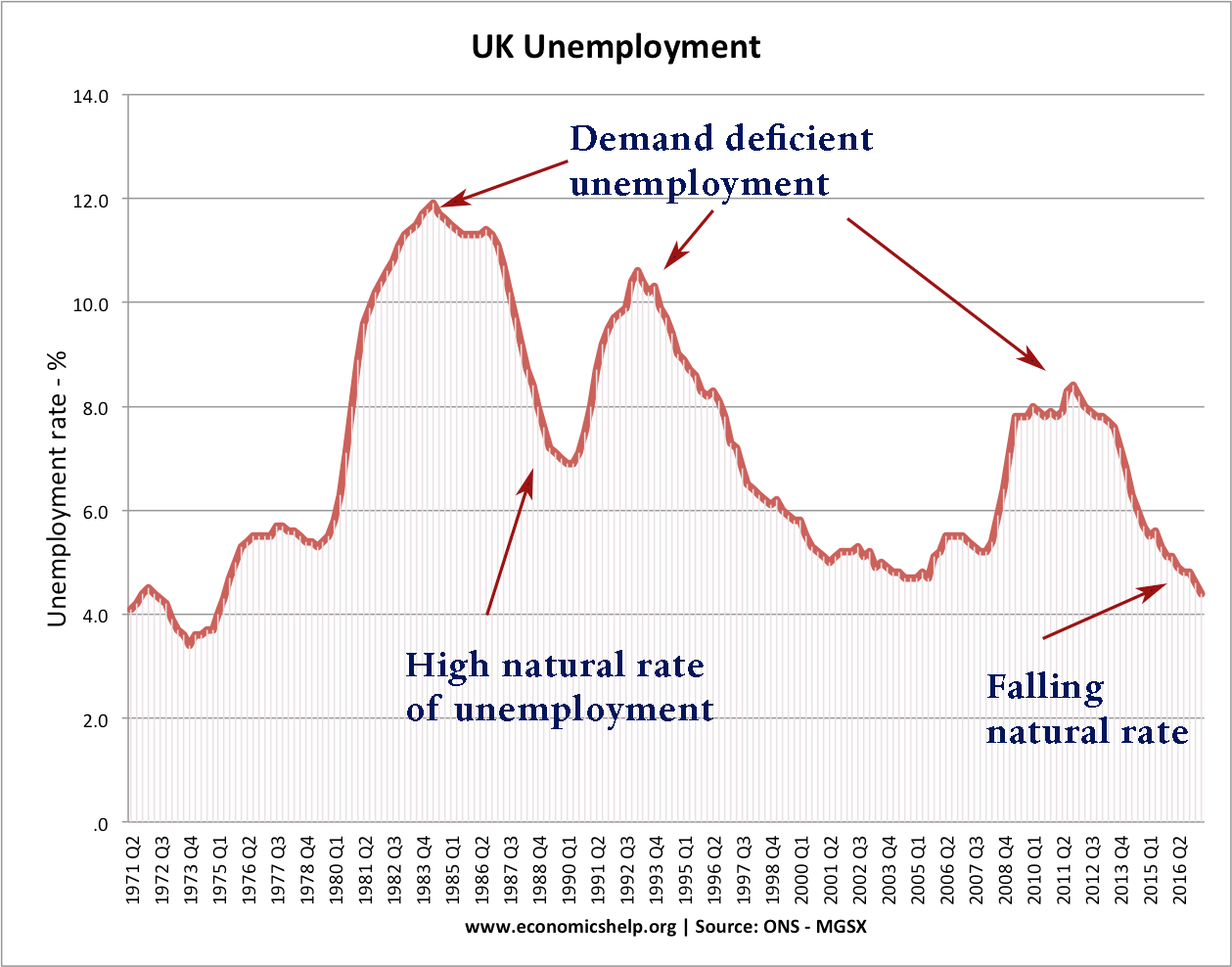
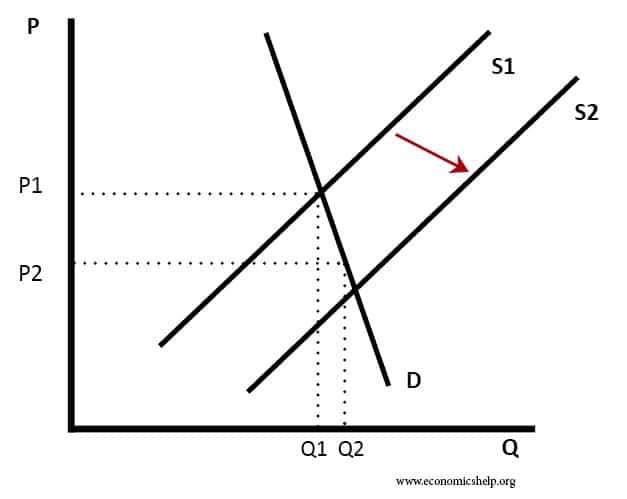
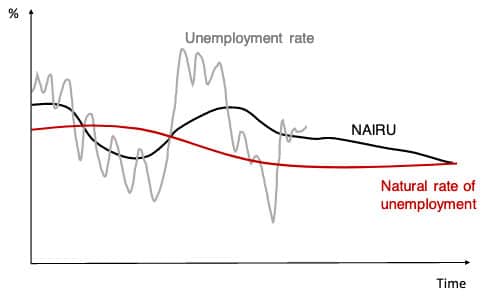
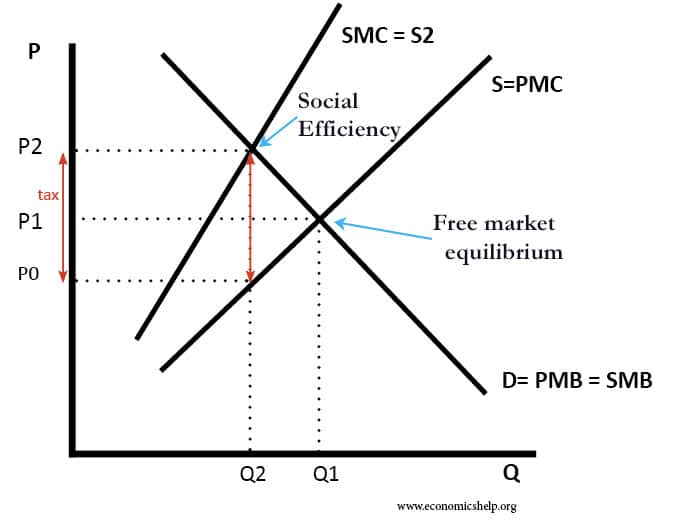
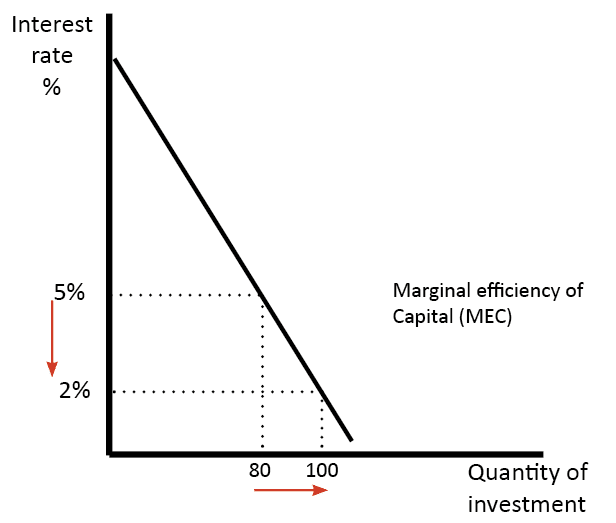
Discuss whether demand side policies will be successful in reducing unemployment?
Demand side policies include expansionary fiscal and monetary policies. For example, the govt could increase Govt spending and lower taxes. G is a component of AD, therefore, this will cause AD to increase, there may also be a multiplier effect causing AD to increase even more than the initial effect Lower tax rates will increase …