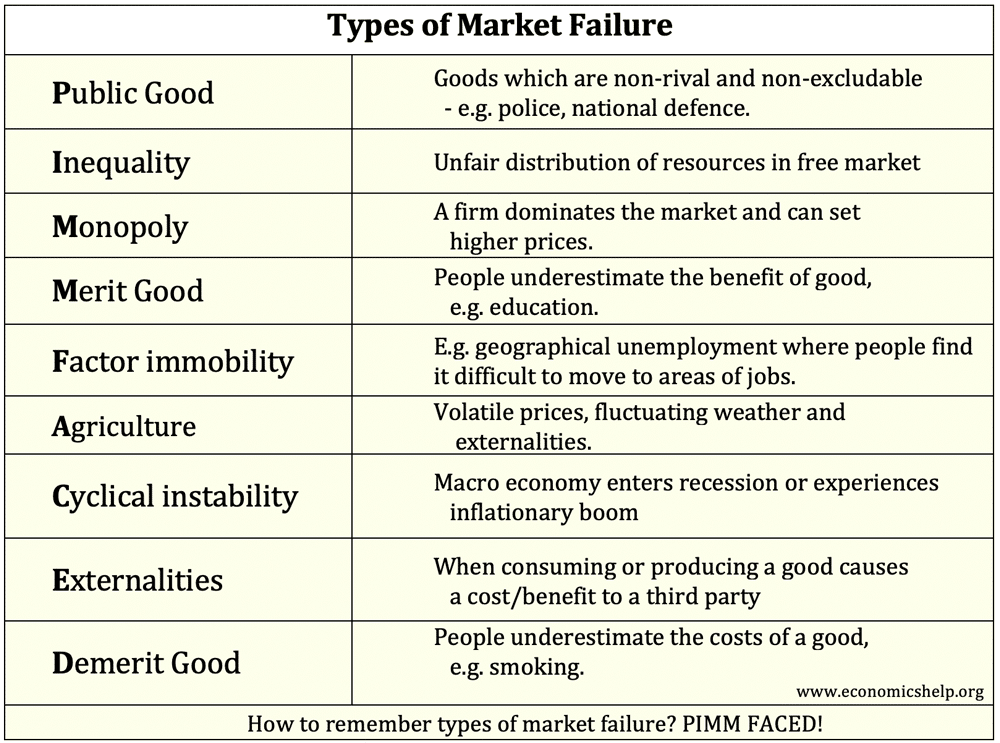
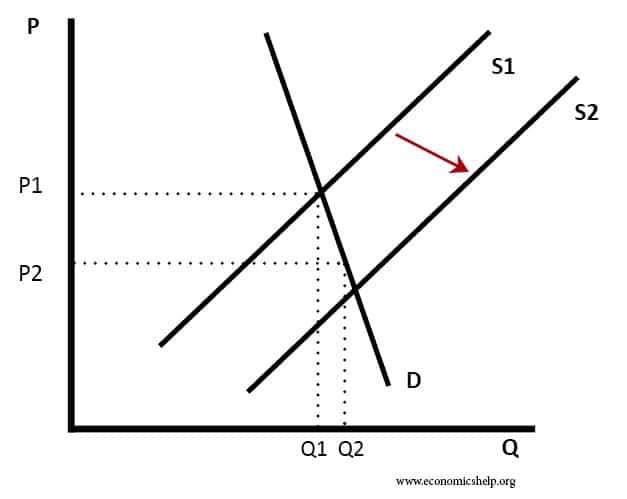
The Role of Supply Side Policies in a Recession
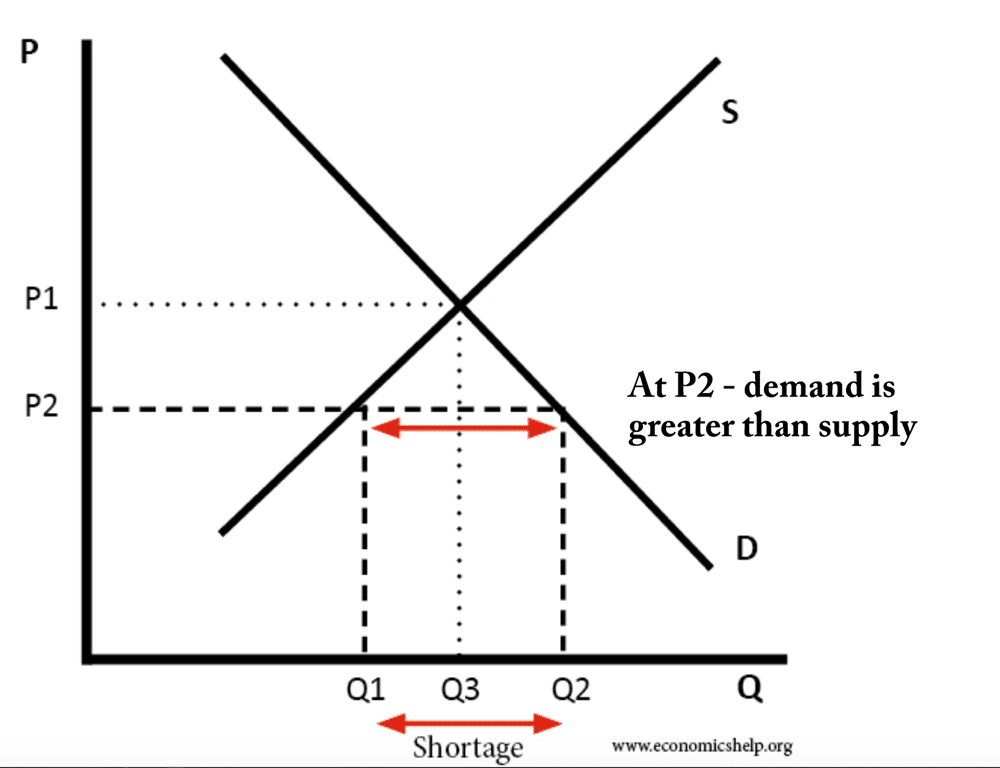
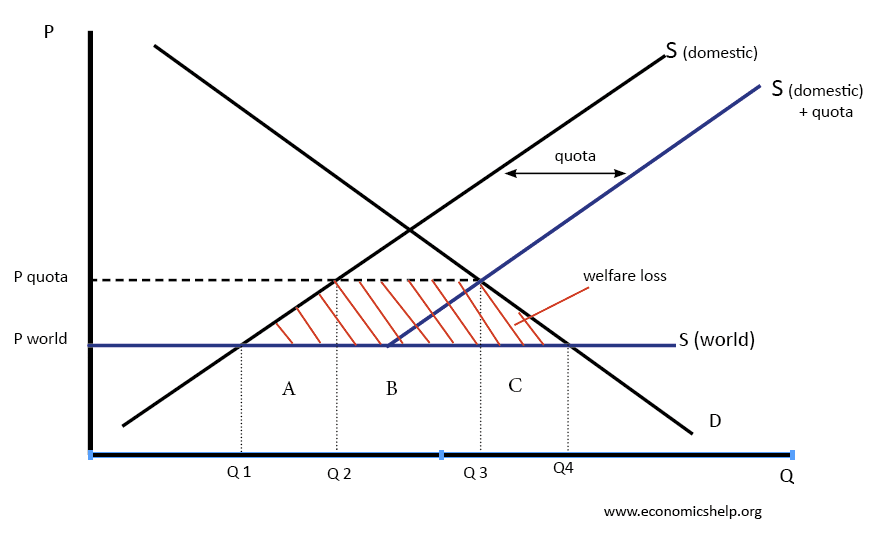
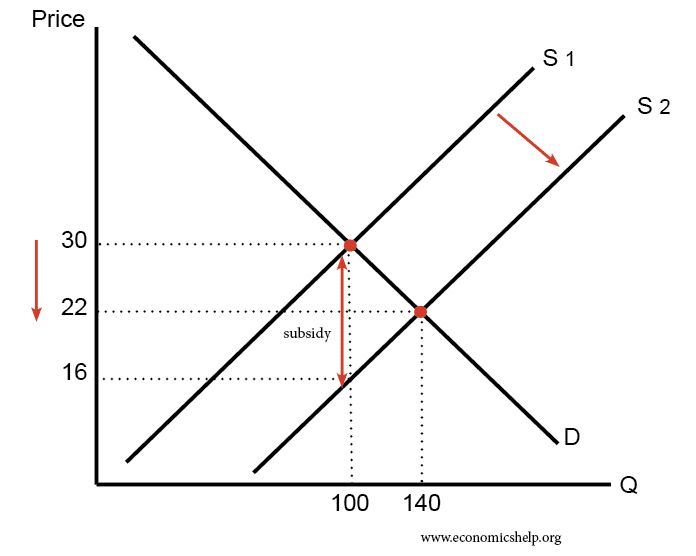
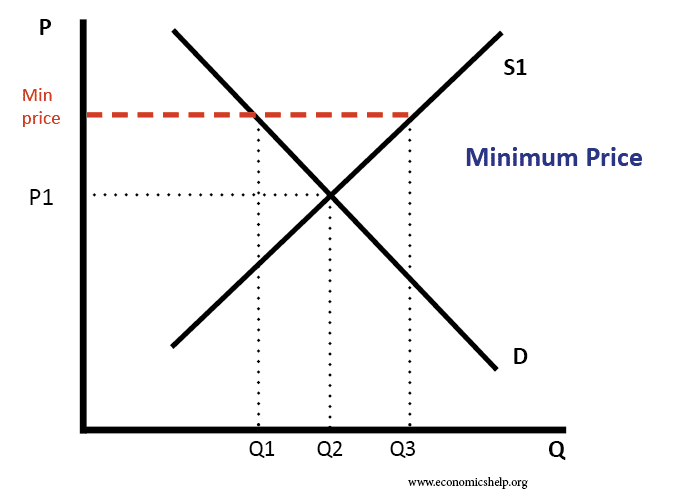
Supply side policies are efforts to increase competitiveness and efficiency in the economy. They can include policies such as tax cuts, privatisation, investment in education and more flexible labour markets. Usually, supply side policies are long-term efforts to increase productivity and the long-run trend rate of growth. The traditional solution to a recession is to …