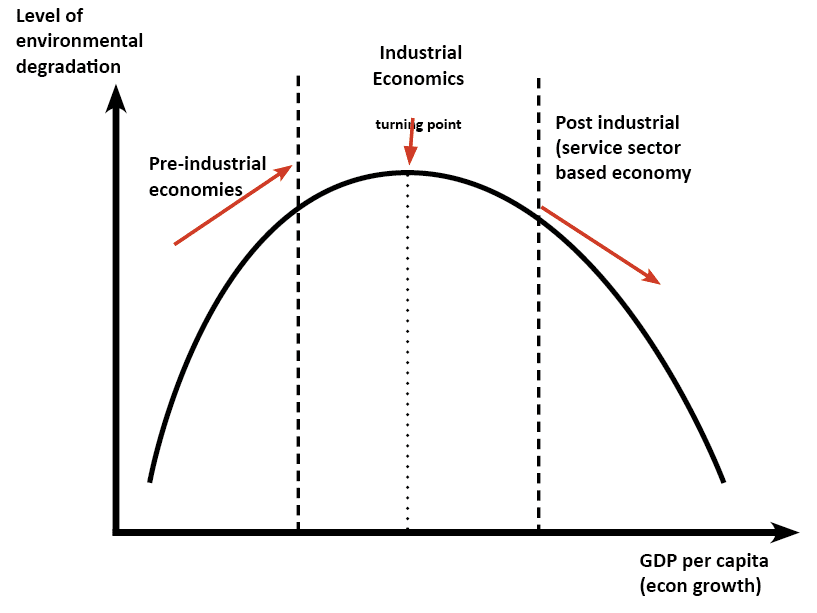
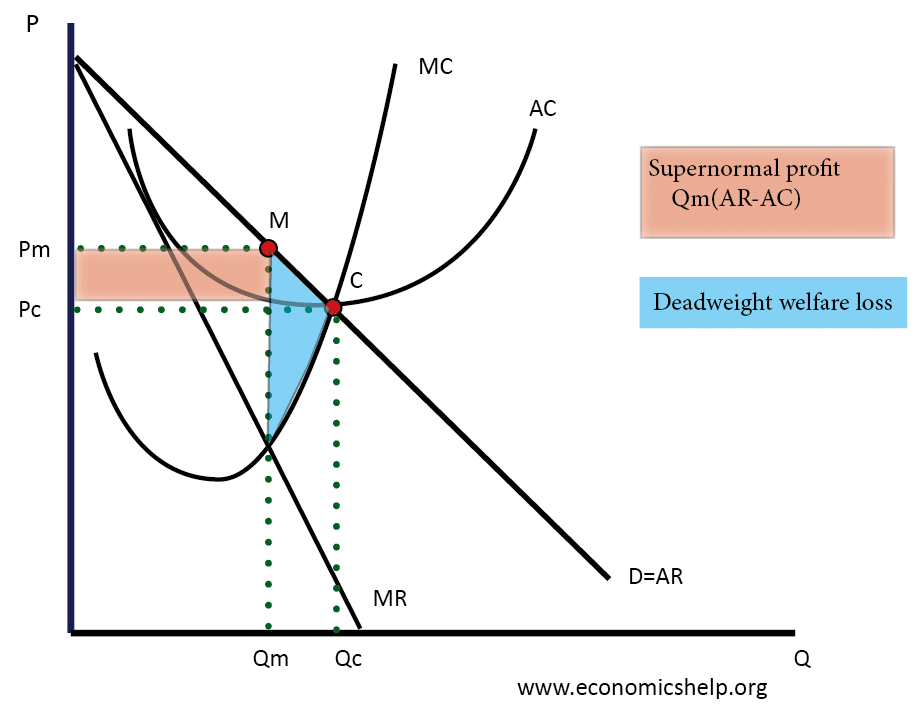
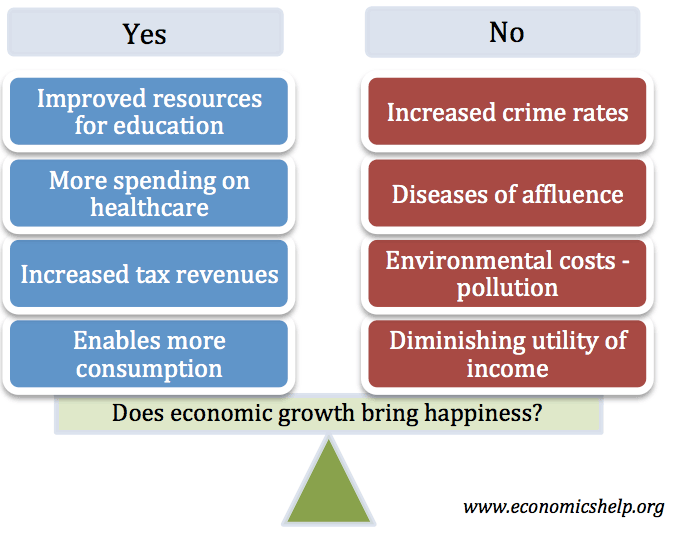
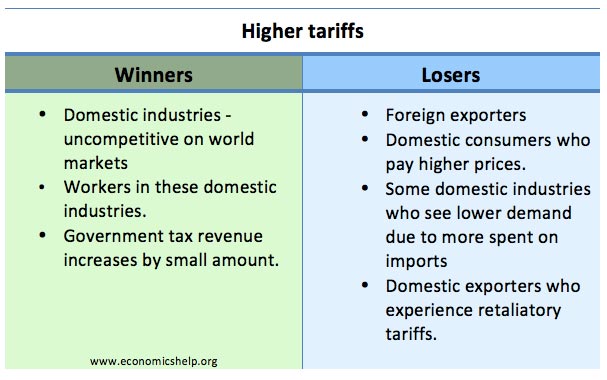
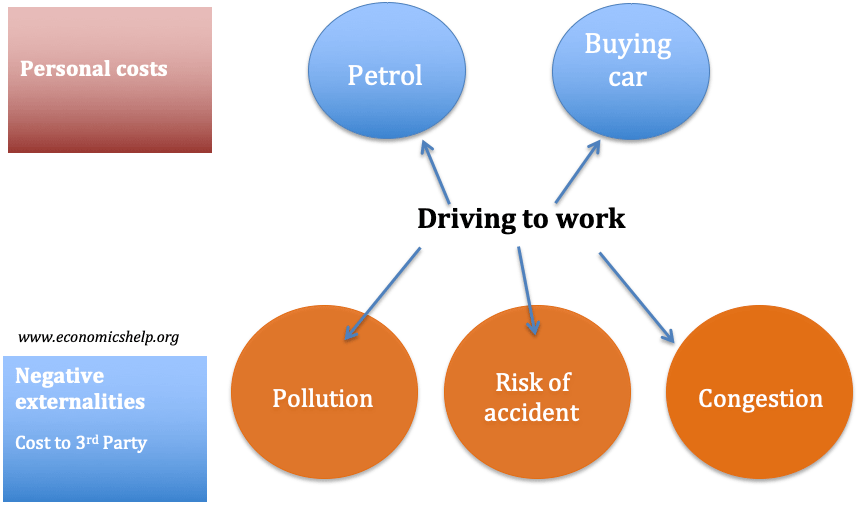
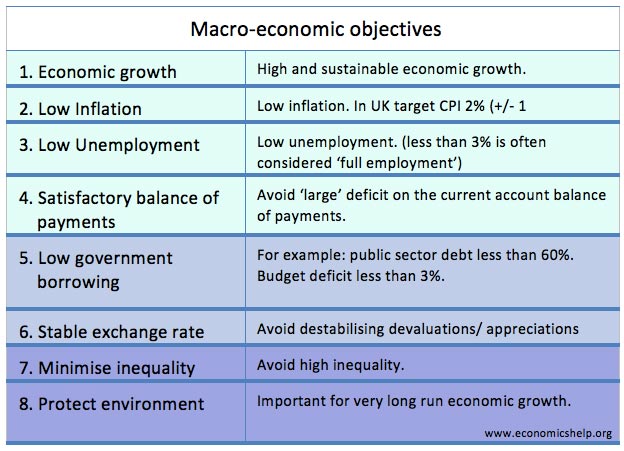
Effects of slower economic growth
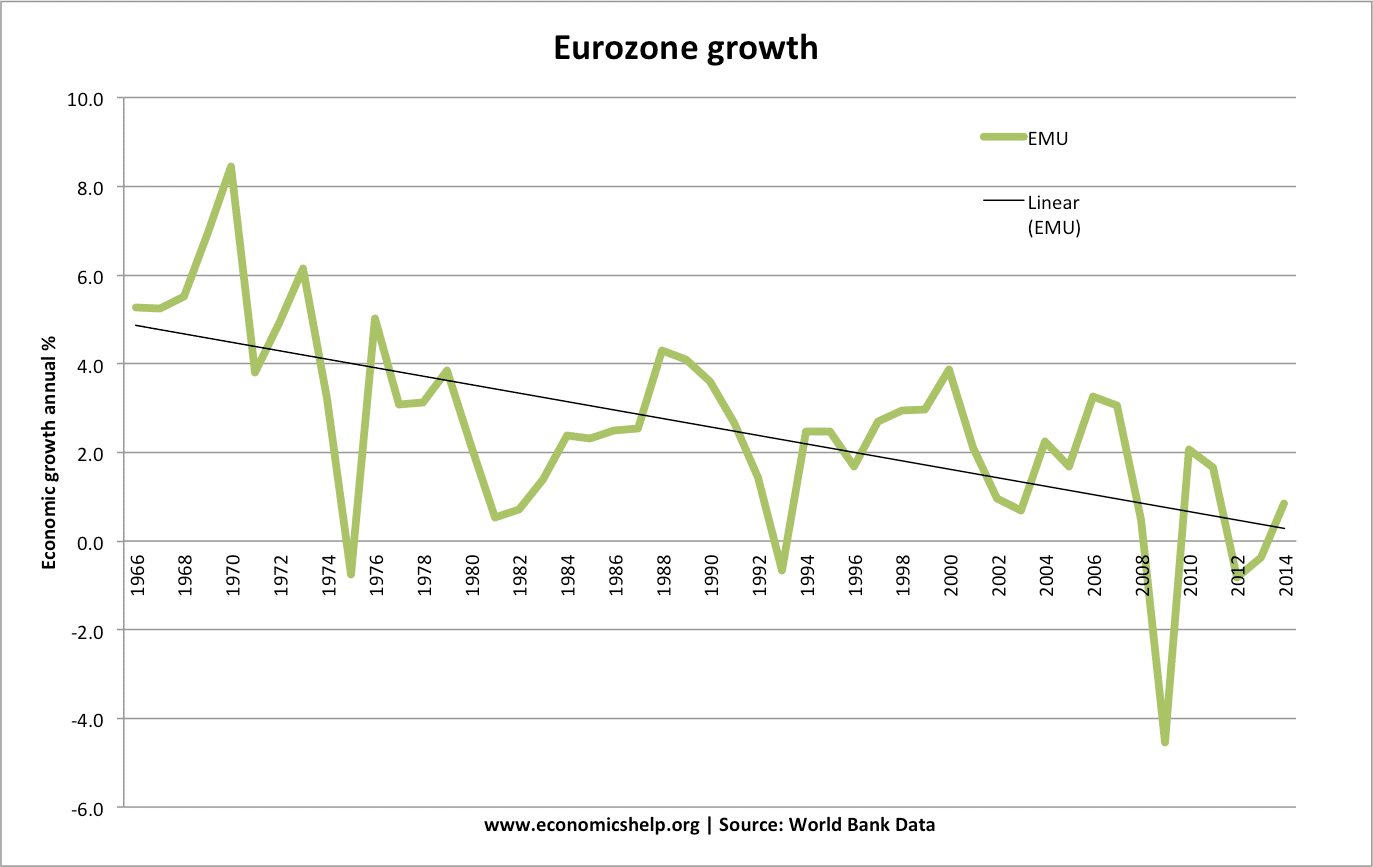
Economic growth means an increase in national income/national output. If we have a slower rate of economic growth – living standards will increase at a slower rate. For example, in the post-war period, western economies grew at 2.5% to 4.% per year. However, since the early 2000s, growth rates have slowed down. This process of …