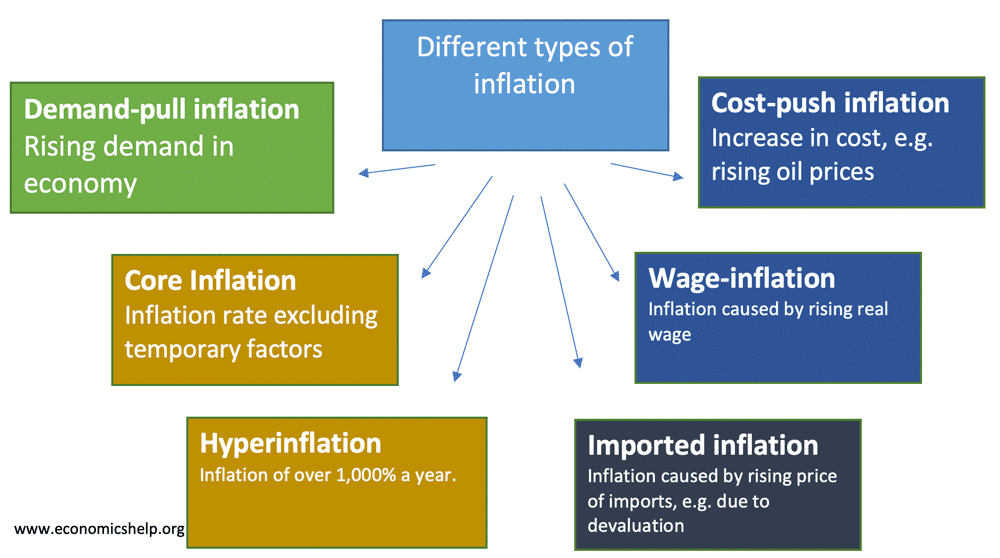
Different types of inflation
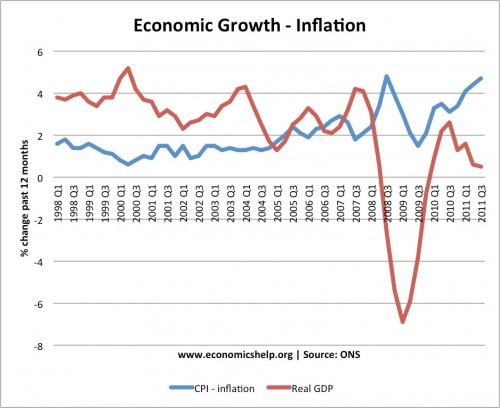
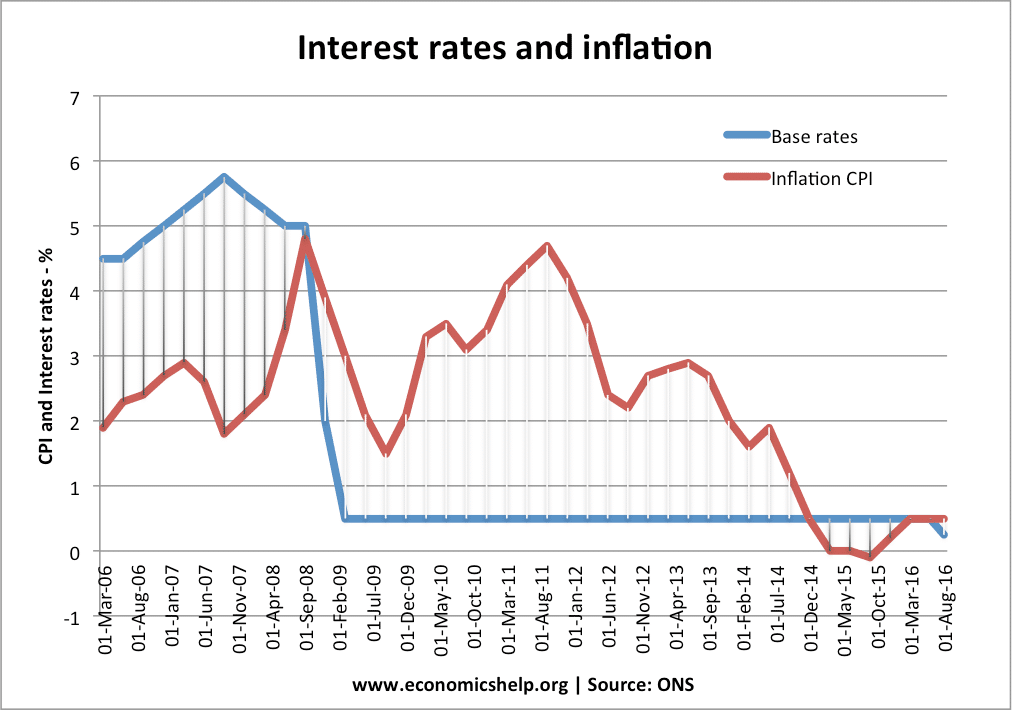
Inflation means a sustained increase in the general price level. The main two types of inflation are Demand-pull inflation – this occurs when the economy grows quickly and starts to ‘overheat’ – Aggregate demand (AD) will be increasing faster than aggregate supply (LRAS). Cost-push inflation – this occurs when there is a rise in the …