Financial Instability Hypothesis
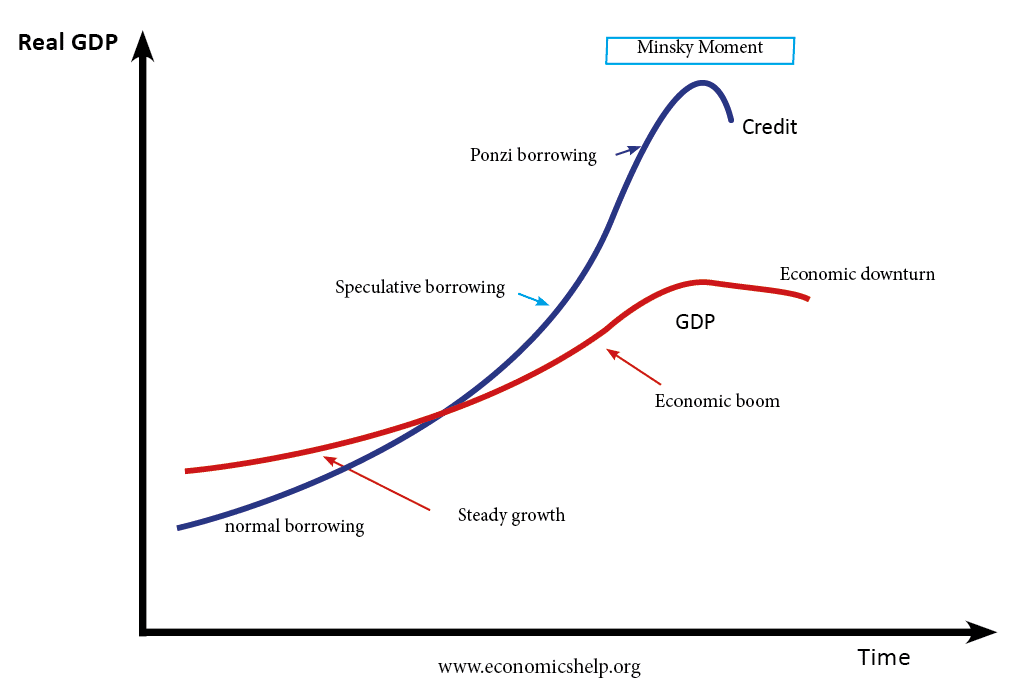
The hypothesis of financial instability was developed by the economist Hyman Minksy. He argued that financial crisis are endemic in capitalism because periods of economic prosperity encouraged borrowers and lender to be progressively reckless. This excess optimism creates financial bubbles and the later busts. Therefore, capitalism is prone to move from periods of financial stability …