Pareto efficiency
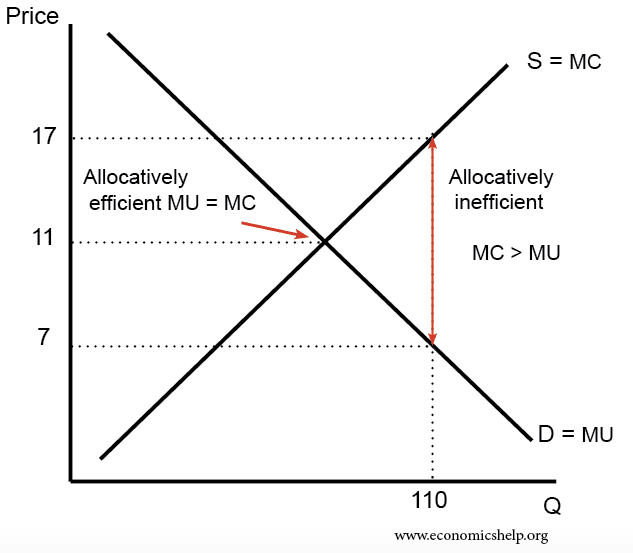
Definition of Pareto efficiency Pareto efficiency is said to occur when it is impossible to make one party better off without making someone worse off. A Pareto improvement is said to occur when at least one individual becomes better off without anyone becoming worse off. Pareto efficiency will occur on a production possibility frontier. When …