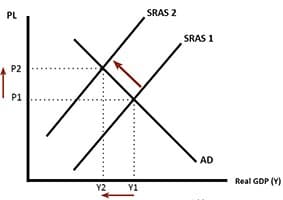
Monopolistic Competition – definition, diagram and examples
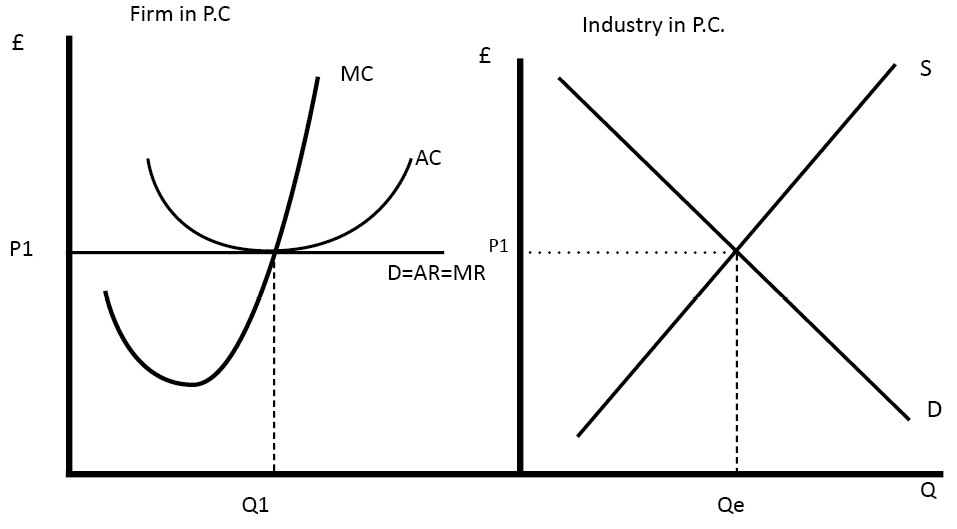
Definition: Monopolistic competition is a market structure which combines elements of monopoly and competitive markets. Essentially a monopolistic competitive market is one with freedom of entry and exit, but firms can differentiate their products. Therefore, they have an inelastic demand curve and so they can set prices. However, because there is freedom of entry, supernormal …