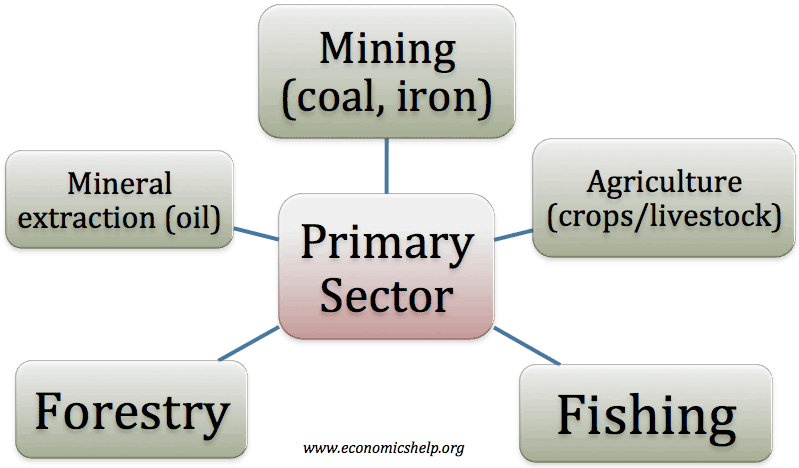
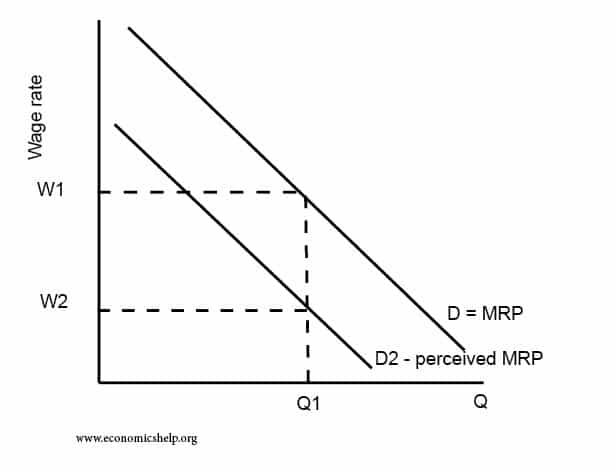
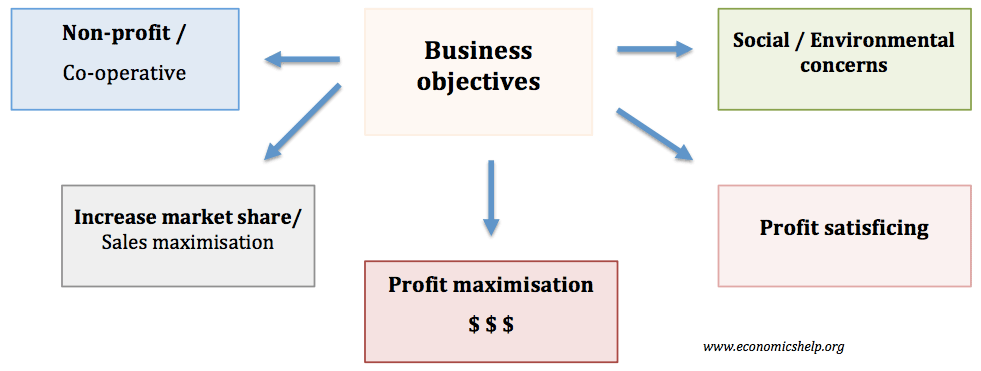
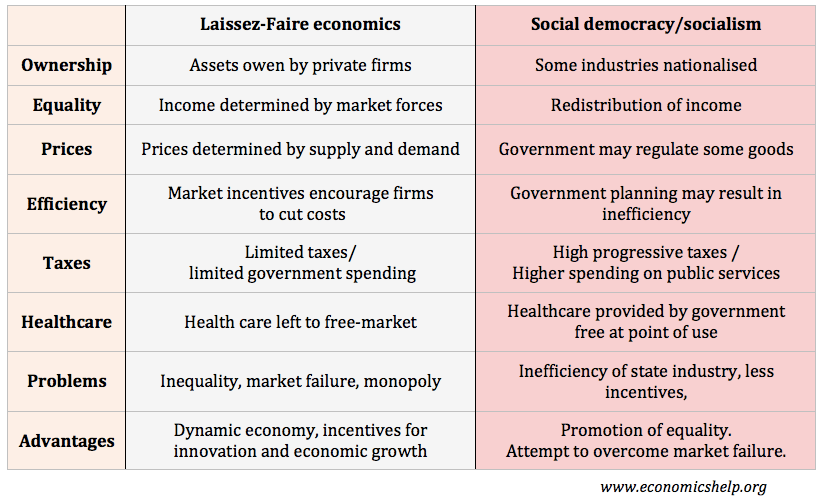
Washington consensus – definition and criticism
The Washington Consensus refers to a set of broadly free market economic ideas, supported by prominent economists and international organisations, such as the IMF, the World Bank, the EU and the US. Essentially, the Washington consensus advocates, free trade, floating exchange rates, free markets and macroeconomic stability. The ten principles originally stated by John Williamson …