Advantages of monopoly
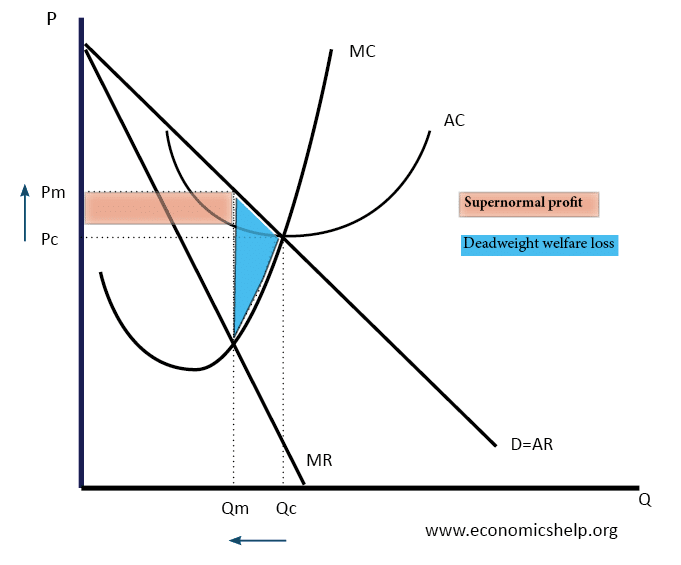
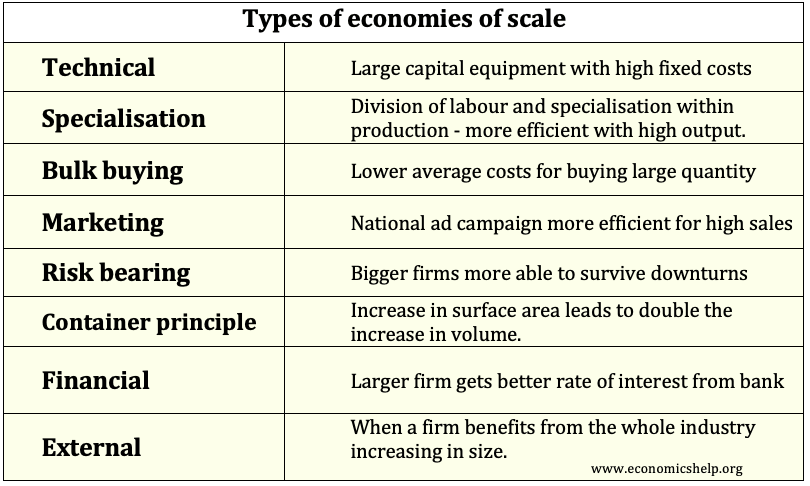
Monopolies are generally considered to have several disadvantages (higher price, fewer incentives to be efficient e.t.c). However, monopolies can also give benefits, such as – economies of scale, (lower average costs) and a greater ability to fund research and development. In certain circumstances, the advantages of monopolies can outweigh their costs. Advantages of Monopoly Research …