Maximum prices – definition, diagrams and examples
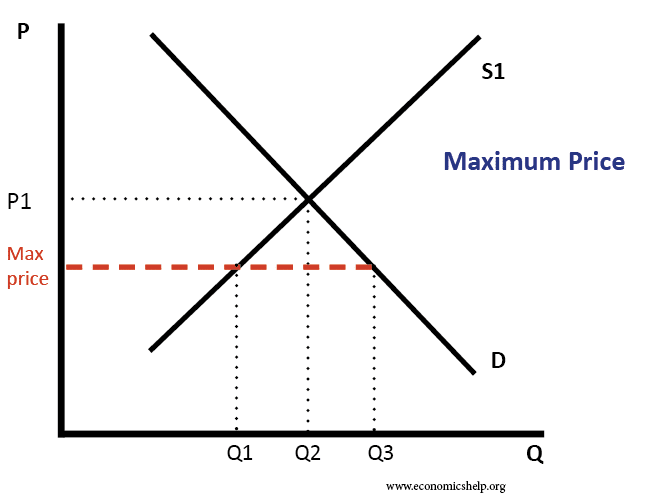
Definition – A maximum price occurs when a government sets a legal limit on the price of a good or service – with the aim of reducing prices below the market equilibrium price. For example, the government may set a maximum price of bread of £1 – or a maximum price of a weekly rent …