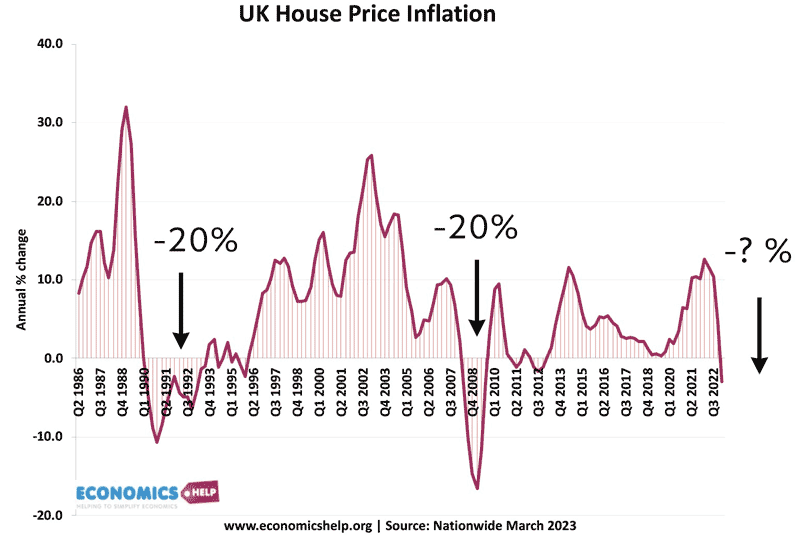
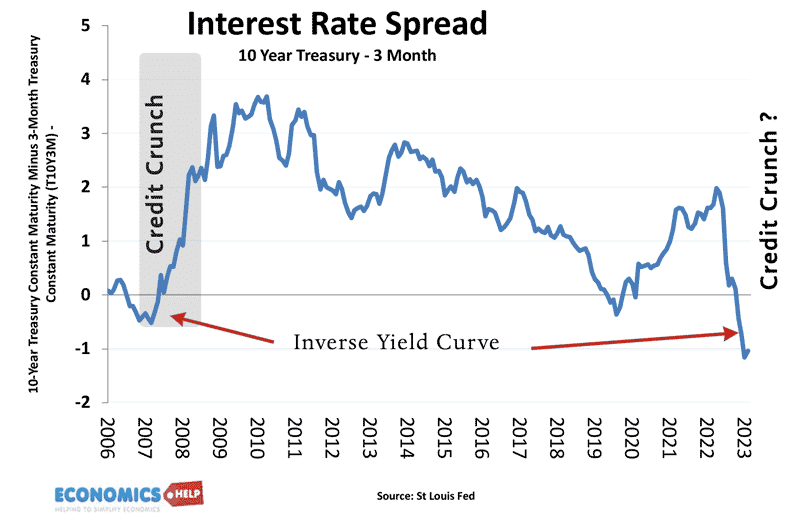
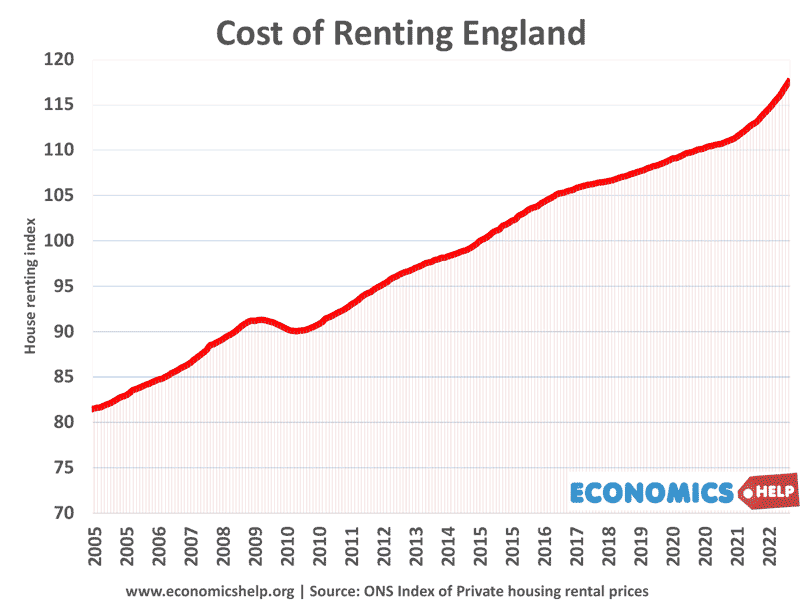
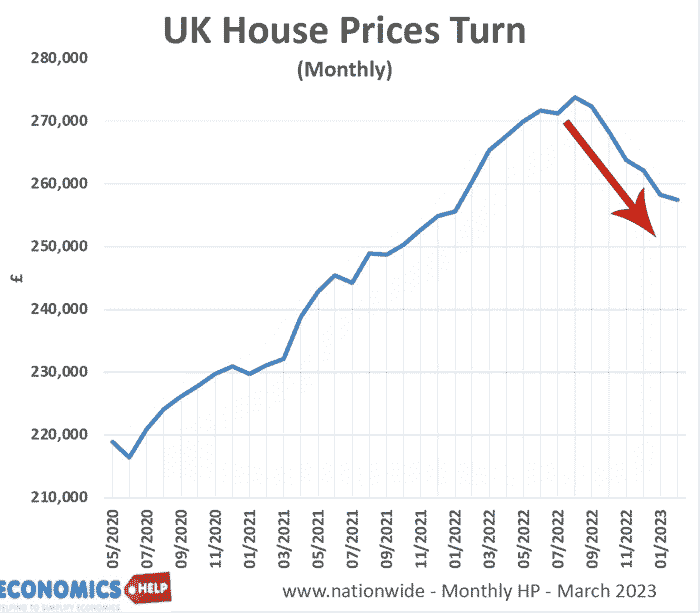
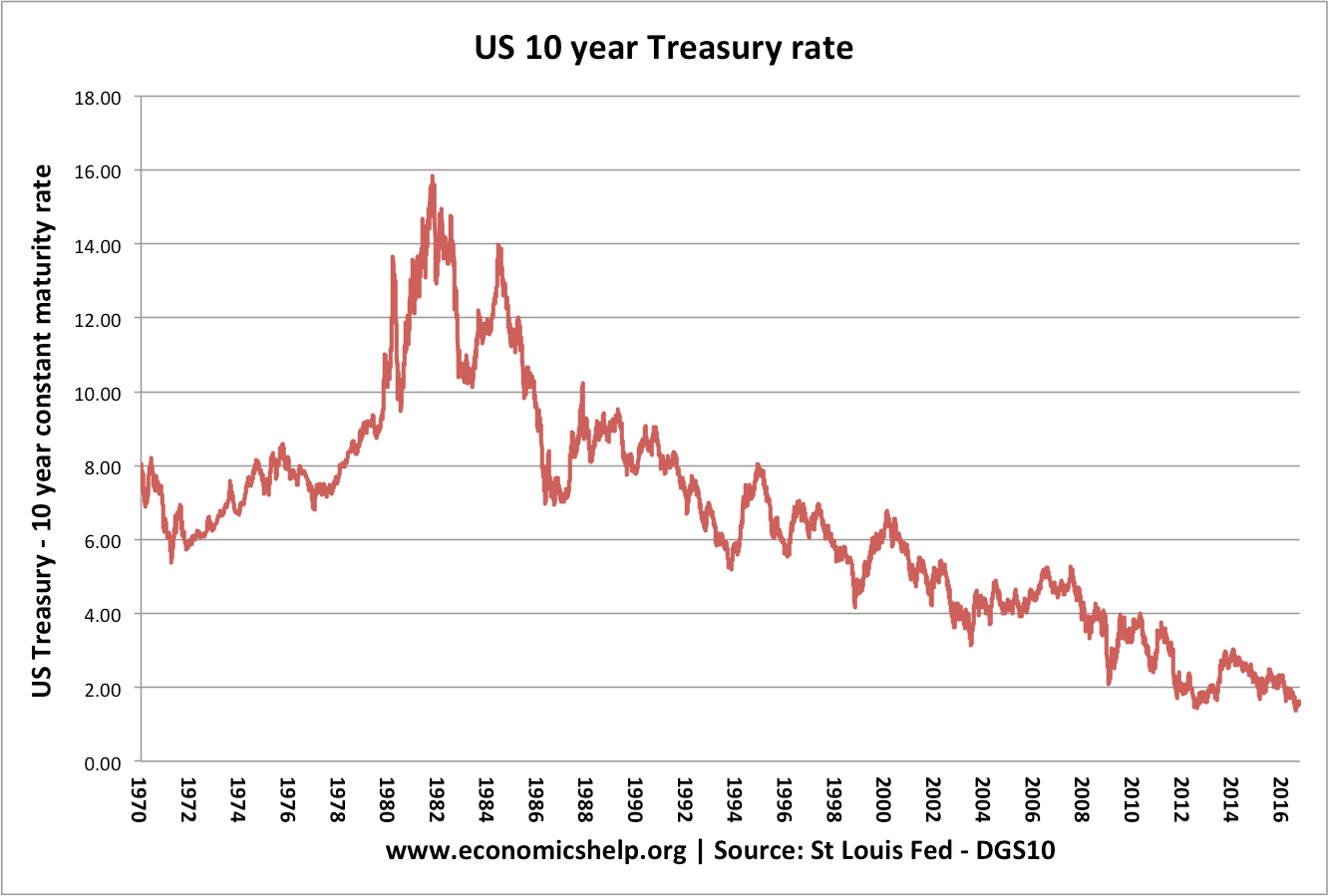
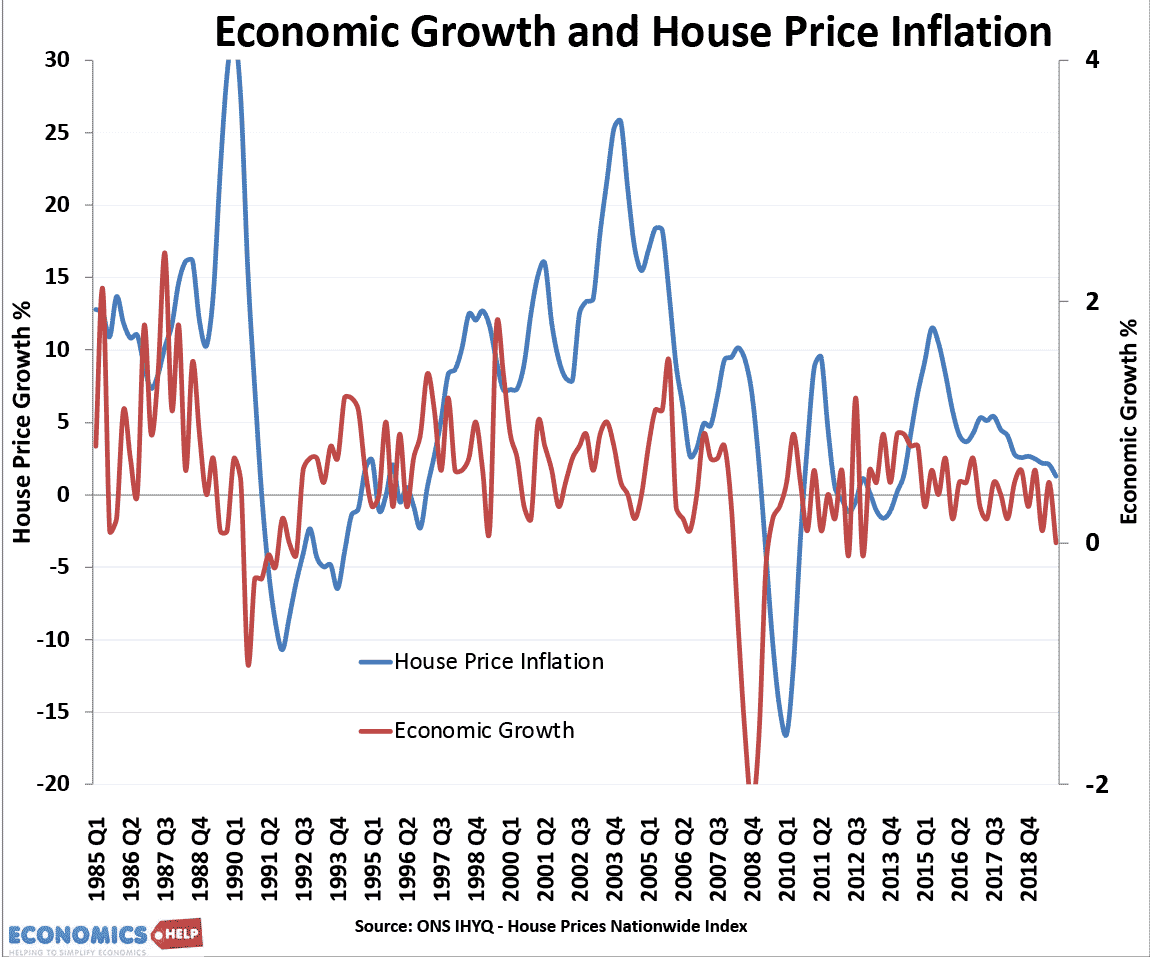
Will House Price Falls in 2023 be like Crashes of 2007 and 1991?
In both 2007 and 1991, house prices fell 20%, will see something similar this year? The really interesting question is whether house prices return to the post-war levels of affordability like after the crashes of 1990 and to a lesser extent 2008. Will The House Price Crash Be Like 1991 and 2008?Watch this video on …