Readers Question: To what extent is it necessary for the government in a developing country over-reliant on tourism to consider the expansion or agriculture and manufacturing?
In theory, the law of comparative advantage states that you should specialise in producing the goods and services where you have a comparative advantage (can produce at the lower opportunity cost). However, this may mean that a country concentrates on producing one particular good or service, and there are numerous drawbacks to relying on just one industry to create jobs and promote growth.
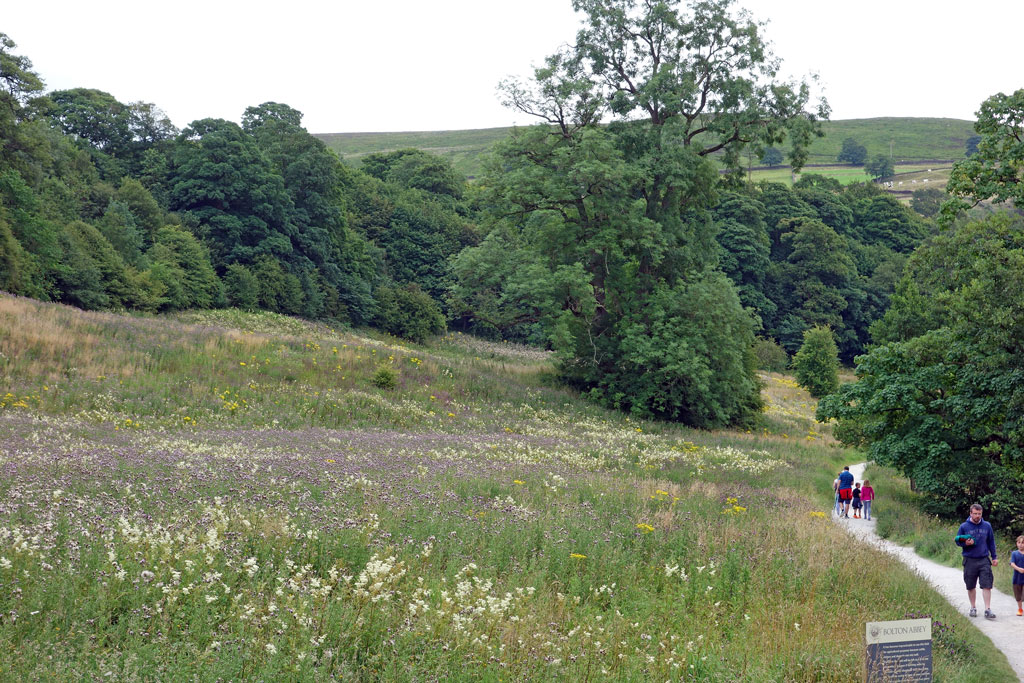
Reasons to diversify away from tourism
- Relying on one industry is risky. Bali relied on tourism to be a major factor in its growth. After a terrorist incident, the number of tourists dropped dramatically and the economy really suffered. If it had diversified the economy and relied less on tourism it would have been in a better position to avoid the problems it faced.
- Changing comparative advantage. At the moment you may not have a comparative advantage in manufacturing. But, that doesn’t mean it will always be the case. It is also important to try develop the economy to enable better technology and productivity improvements. Developing economies may have a current (static) comparative advantage in the labour-intensive tourism industry, but this will change over time, and it would be a mistake to get stuck in over-developing tourism
- Diversification and investment can act as a spur to growth.
- Tourism can place high environmental costs on areas of outstanding natural beauty. Tourism leads to over-use of resources and increases pollution and congestion.
- Tourism can diminish the quality of life for the local population who experience greater congestion due to the influx of tourists.
- Tourism can increase the cost of living and renting. For example, the growth of Airbnb means that property values have increased as landlords want to buy properties to be able to let out to tourists. But, the downside of this is that locals then struggle to afford the prices of living in popular areas.
- Tourism is a very seasonal industry. During winter or summer months, it can lead to seasonal unemployment.