Readers question: What is Austerity?
Simple definition of Austerity
- Austerity involves policies to reduce government spending (or higher taxes) in order to try and reduce government budget deficits – during a period of weak economic growth.
Austerity policies are often associated with higher unemployment and lower economic growth.
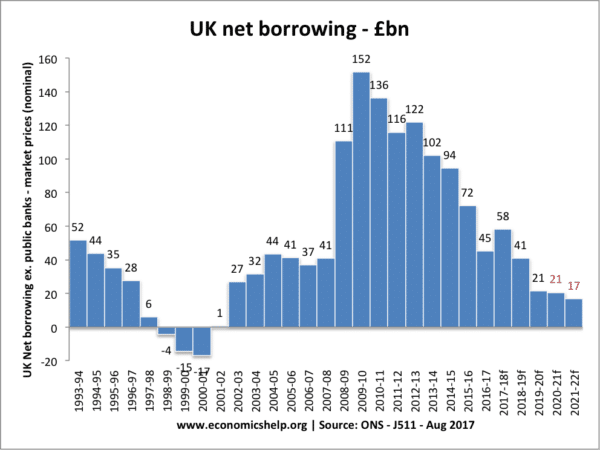
Austerity policies (and automatic stablisers) have reduced levels of government borrowing since 2010.
More complex points and definitions of austerity
The term austerity is more likely to be used when government spending cuts and higher taxes occur during a recession or period of very weak economic growth. Austerity implies that spending cuts and tax increases are highly likely to have an adverse impact on aggregate demand and economic growth. For example, if the government increased taxes during an economic boom, this would probably not be referred to as austerity. But, if the government cut spending during a period of negative growth, this would be referred to as austerity policies.
What constitutes actual austerity?
- A simple definition of austerity implies actual spending cuts. However, some may refer to austerity policies – even if there has just been a limit in the growth of government spending. For example, in the past 10 years, government spending may have increased on average by 3% in real terms. If the government now freezes public sector spending, this may be termed ‘austerity policies’ – because government spending is not increasing at the same rate as previously.