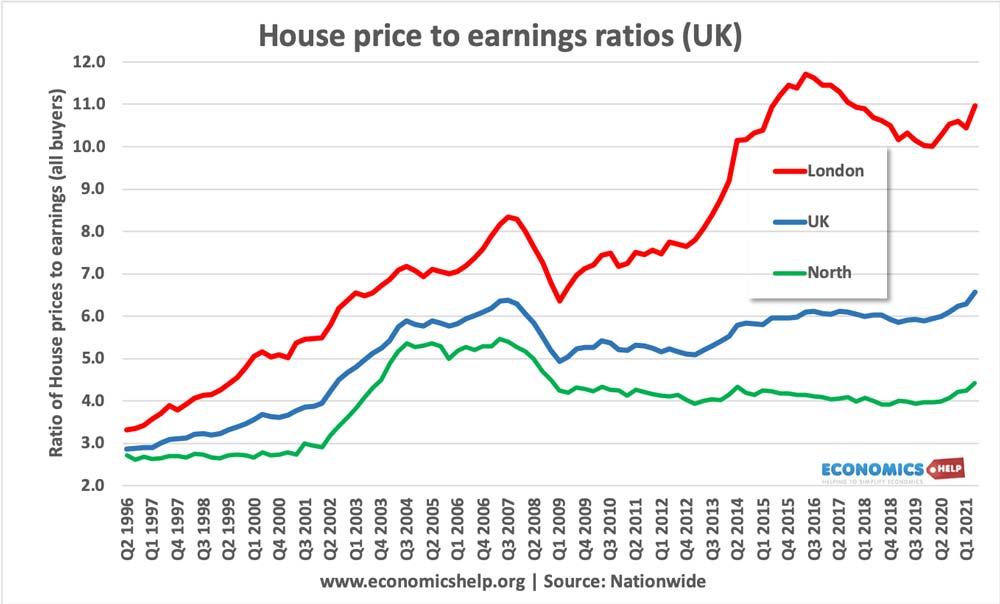
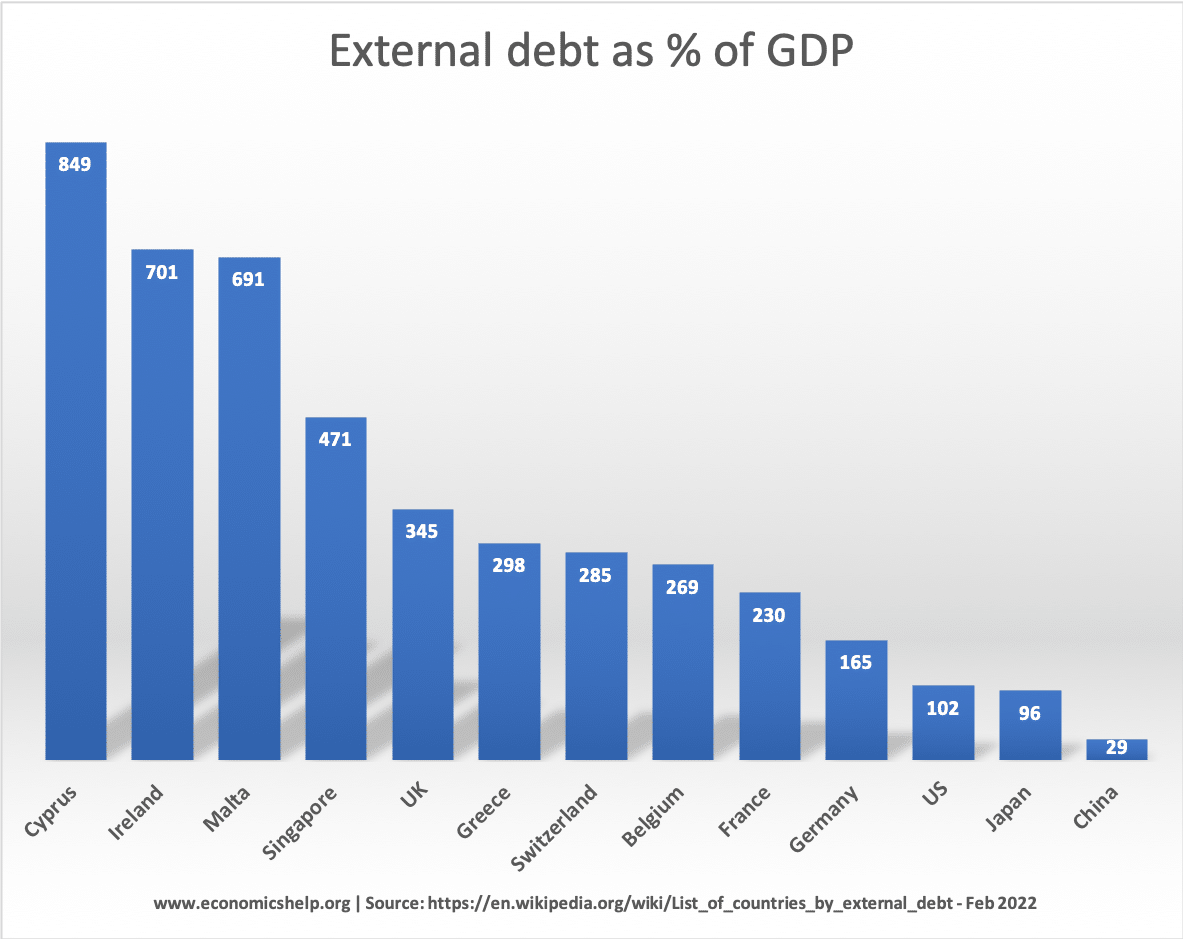
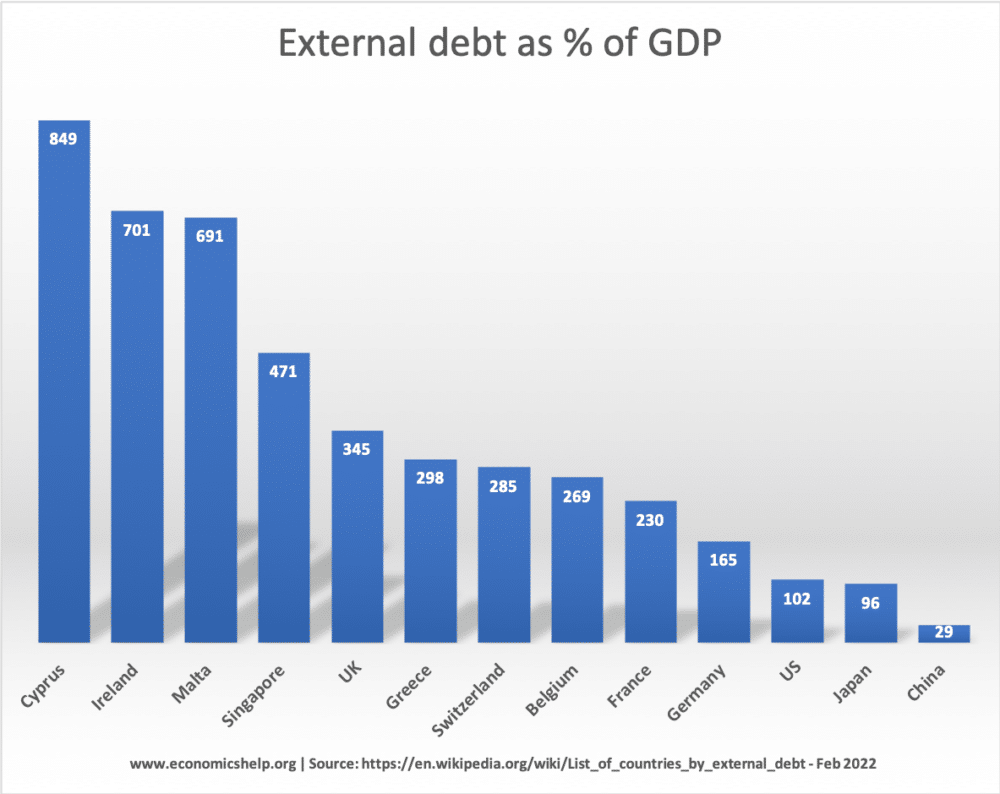
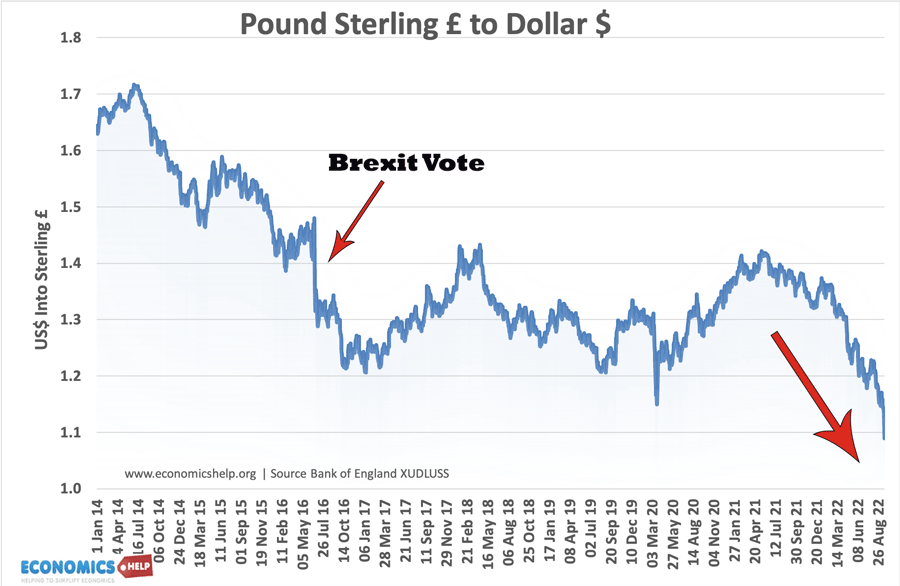
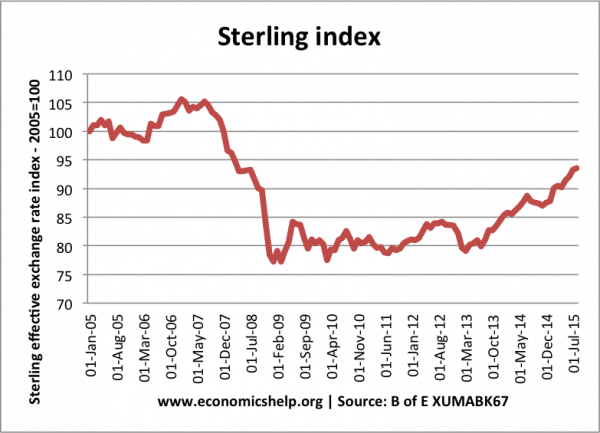
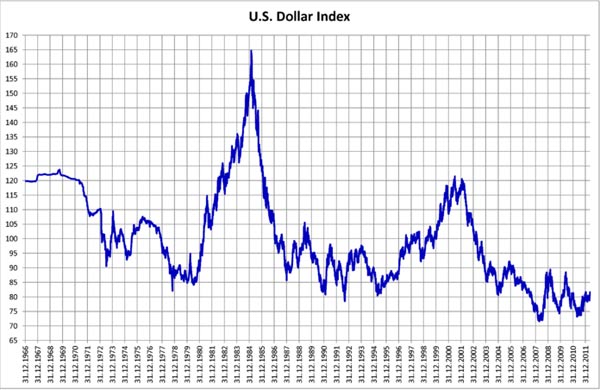
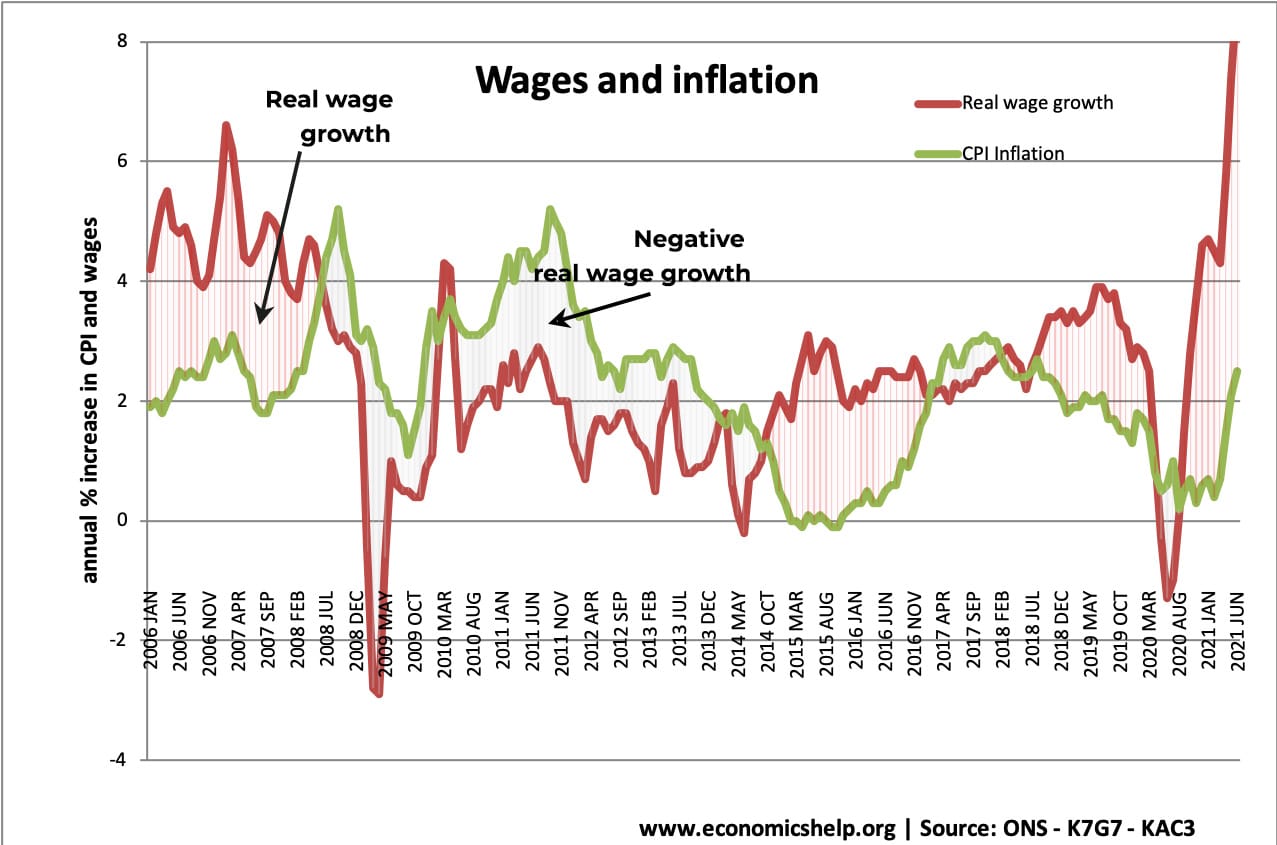
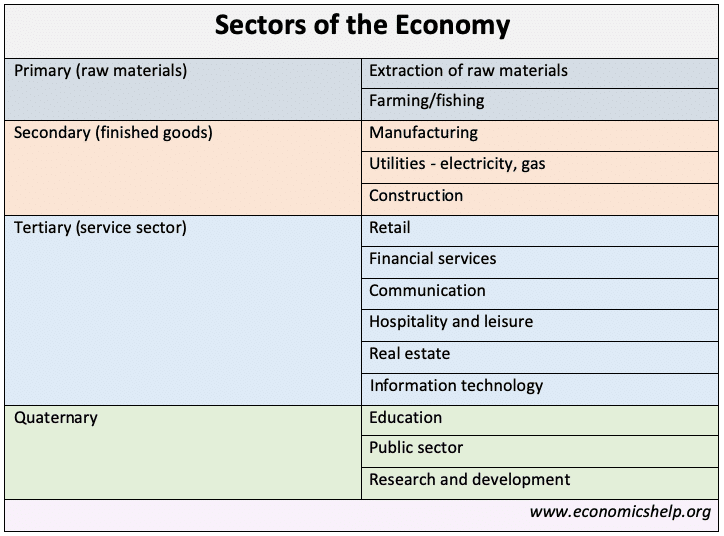
External debt is the total public (government) and private debt owed to non-residents repayable in internationally accepted currencies, goods, or services. This is gross (total) external debt. It does not measure net debt.
External debt is different to measures of public (government) debt. See: List of national debt by country.
Some countries with very high levels of external debt, also have very high levels of external credit. For example, Ireland, United Kingdom, Switzerland and Singapore have high levels of assets – i.e. they hold the external debt of other countries. In fact, they are net international creditors because there assets are greater than their debt levels.
Countries with large banking systems tend to have higher levels of external debt because they correspondingly hold more international assets. The problem comes when the assets they hold fall in value.
However, some countries can have high external debt because of past borrowing requirements and high levels of government debt. For example, Greece has one of the highest levels of external debt 298% of GDP. This is largely due to the debt crisis of 2010 onwards where Greek debt became overwhelming and they required foreign borrowing.
External debt can be problematic for developing countries if interest payments on their external debt levels impact on a countries ability to invest and spend on current public services.