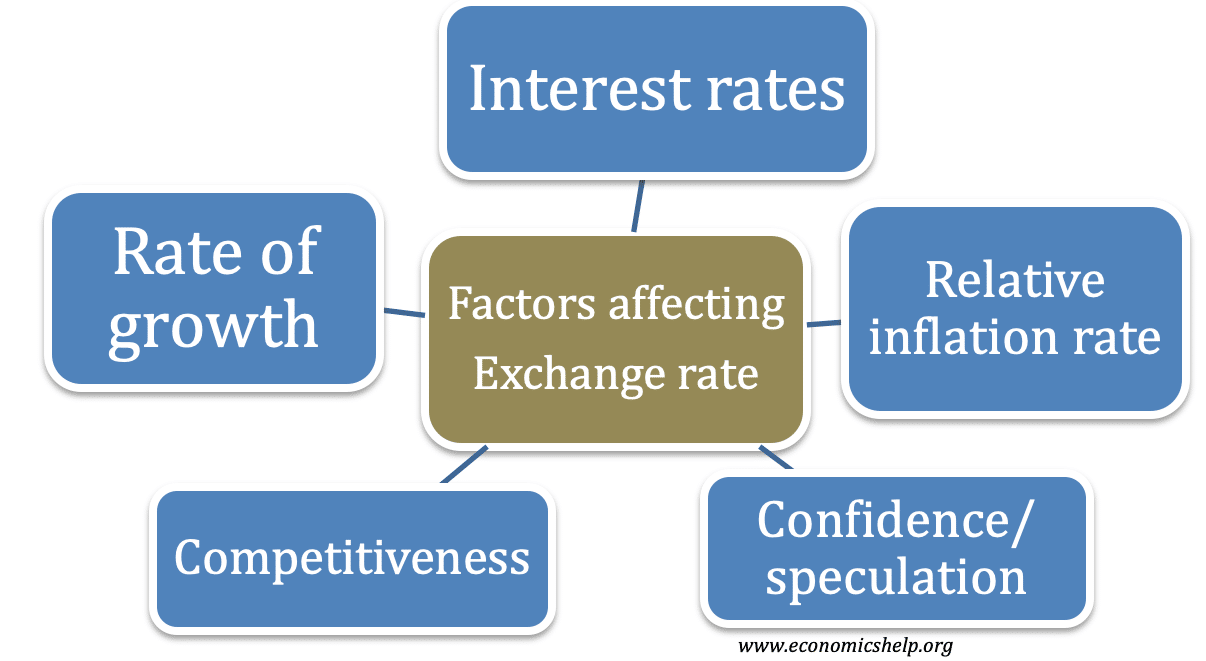
A summary for understanding exchange rates. Factors that affect exchange rates and the impact of exchange rates on the economy.
Terminology
- Depreciation/devaluation – fall in value of exchange rate – exchange rate becomes weaker (see also: definition of devaluation and depreciation)
- Appreciation – increase in the value of exchange rate – exchange rate becomes stronger.
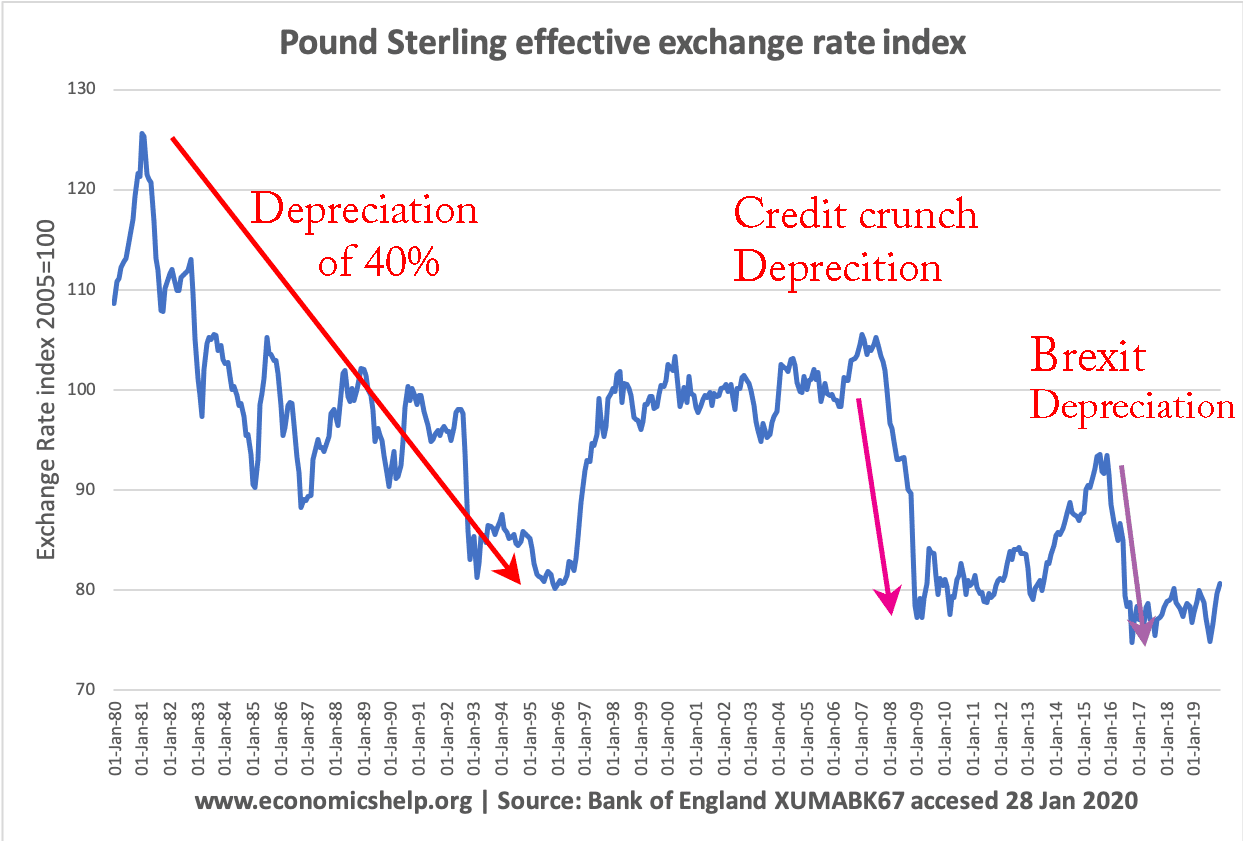
Example of Pound Sterling depreciating against the Dollar
- £1 used to equal $2.
- Now £1 is only equal to $1.75
Video on Exchange rates
What is the effect of a depreciation in the value of the Pound?
- Buying goods from America becomes more expensive.
- If a meal cost $10, it used to require £5 (10/2) for a British tourist.
- But, now after the depreciation, the $10 meal will cost £5.71 (10/1.75)
- The depreciation in the pound may discourage British tourists to travel to the US.
- It makes US imports into the UK more expensive, so it may reduce UK imports
- UK exports will become relatively more competitive. It is cheaper for Americans to buy UK goods, so the quantity of exports should increase.
- UK inflation will increase. Imported goods are more expensive (cost push inflation). Also, British goods are more attractive causing a rise in demand (demand pull inflation)
Summary of depreciation
- A depreciation in exchange rate makes exports more competitive and imports more expensive
- A depreciation helps UK exporters and improves UK growth prospects, but causes higher prices and inflation.