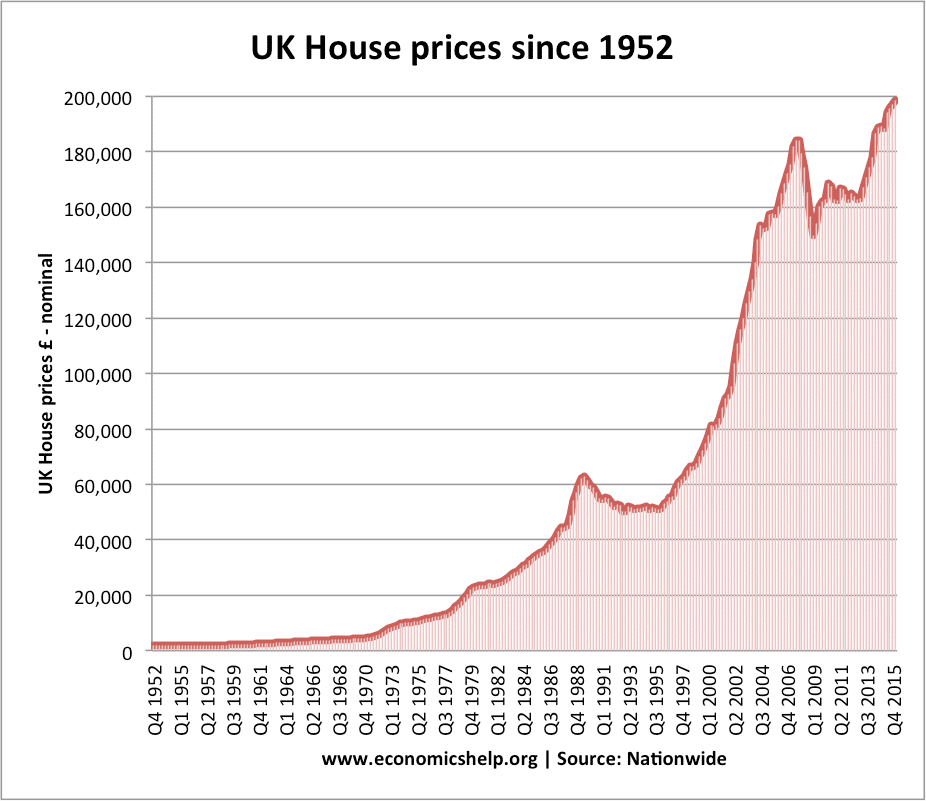
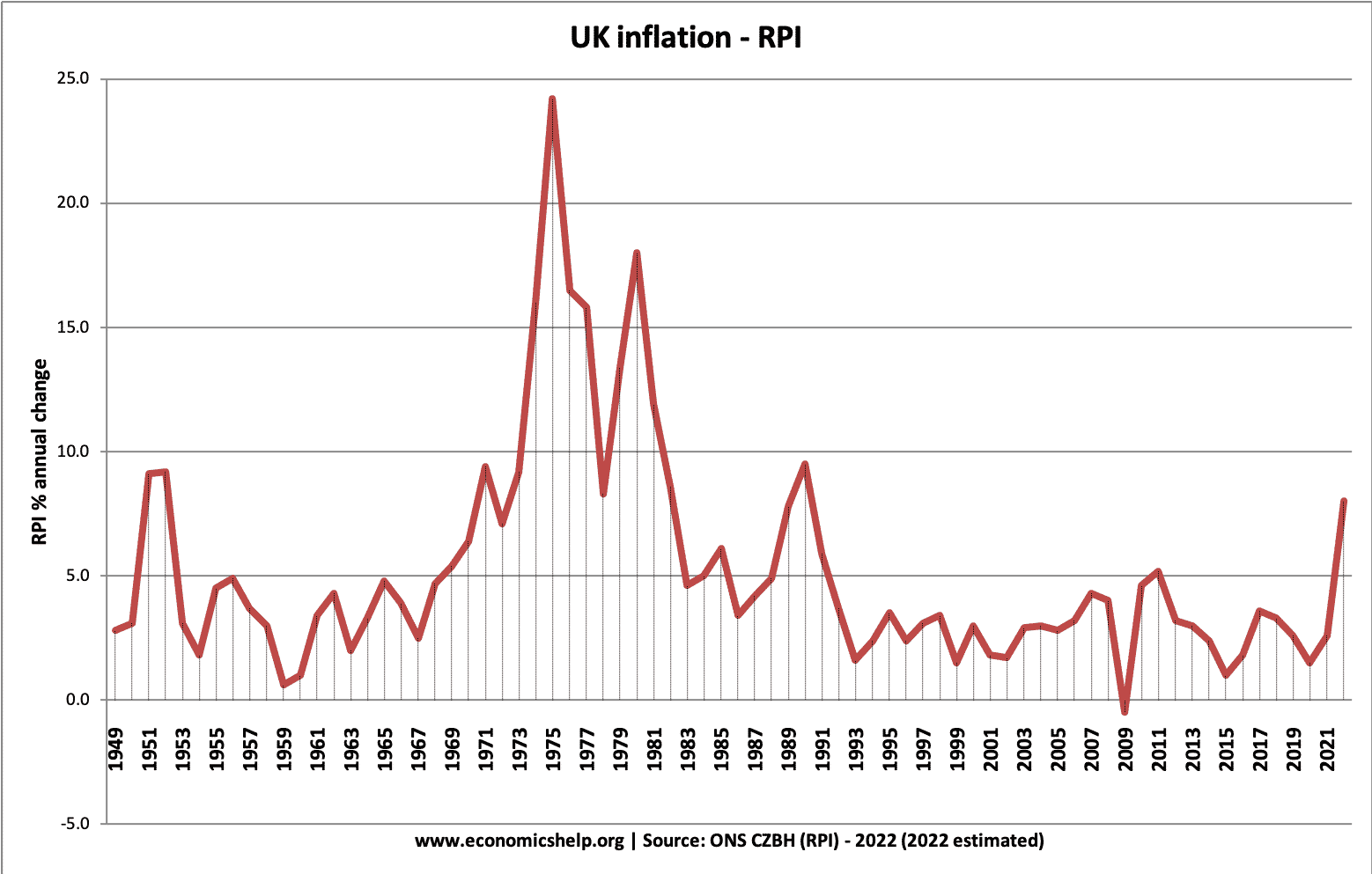
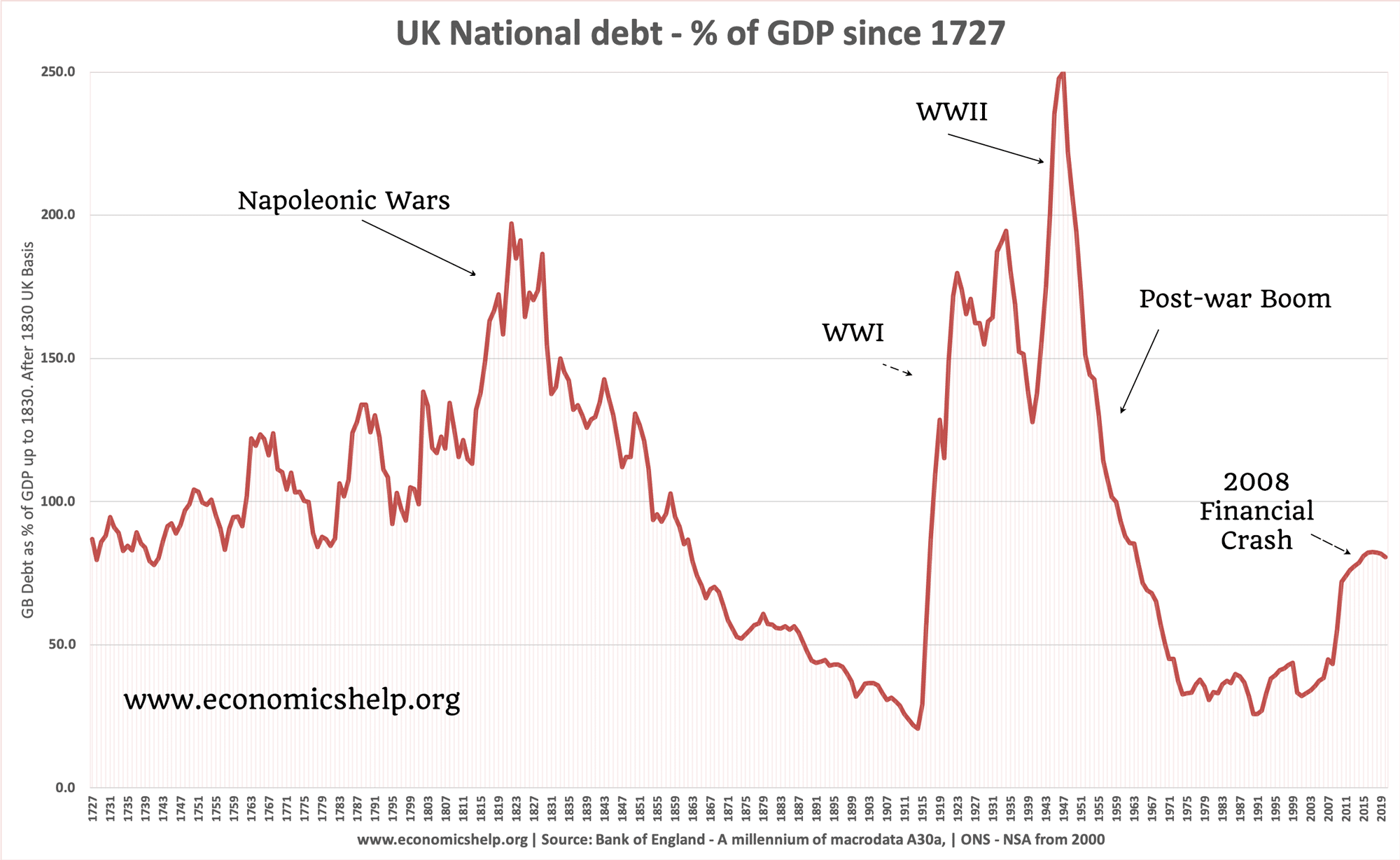
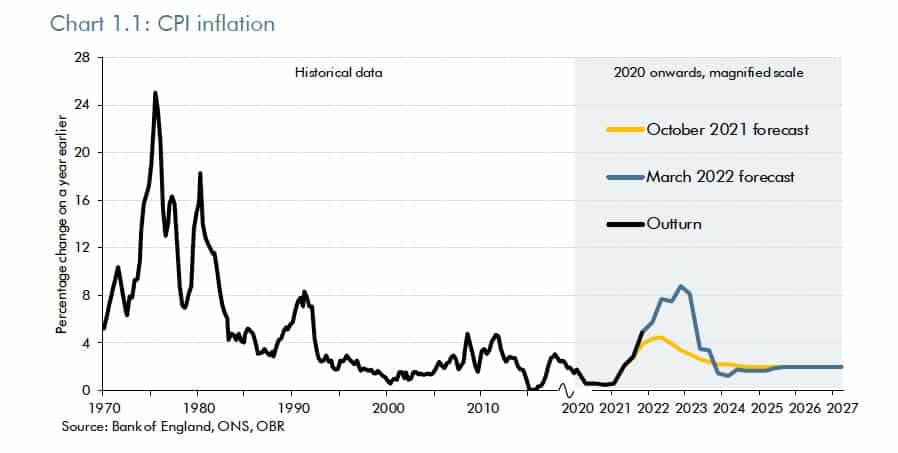
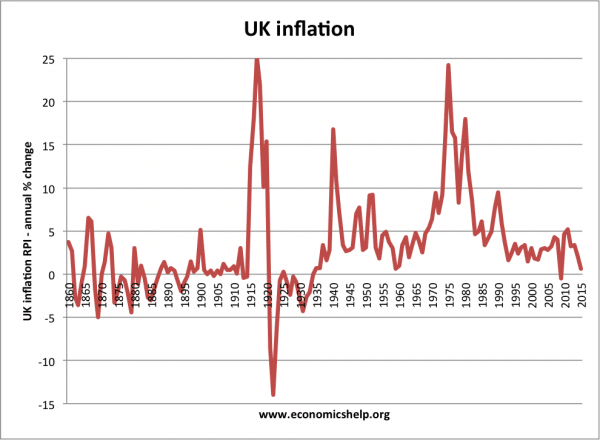
The UK has avoided any situation of hyperinflation. The highest rates of inflation were after the Napoleonic War in the early nineteenth century. During the First World war (25%) and in the 1970s where inflation rose due to a rise in oil prices and strong wage growth.
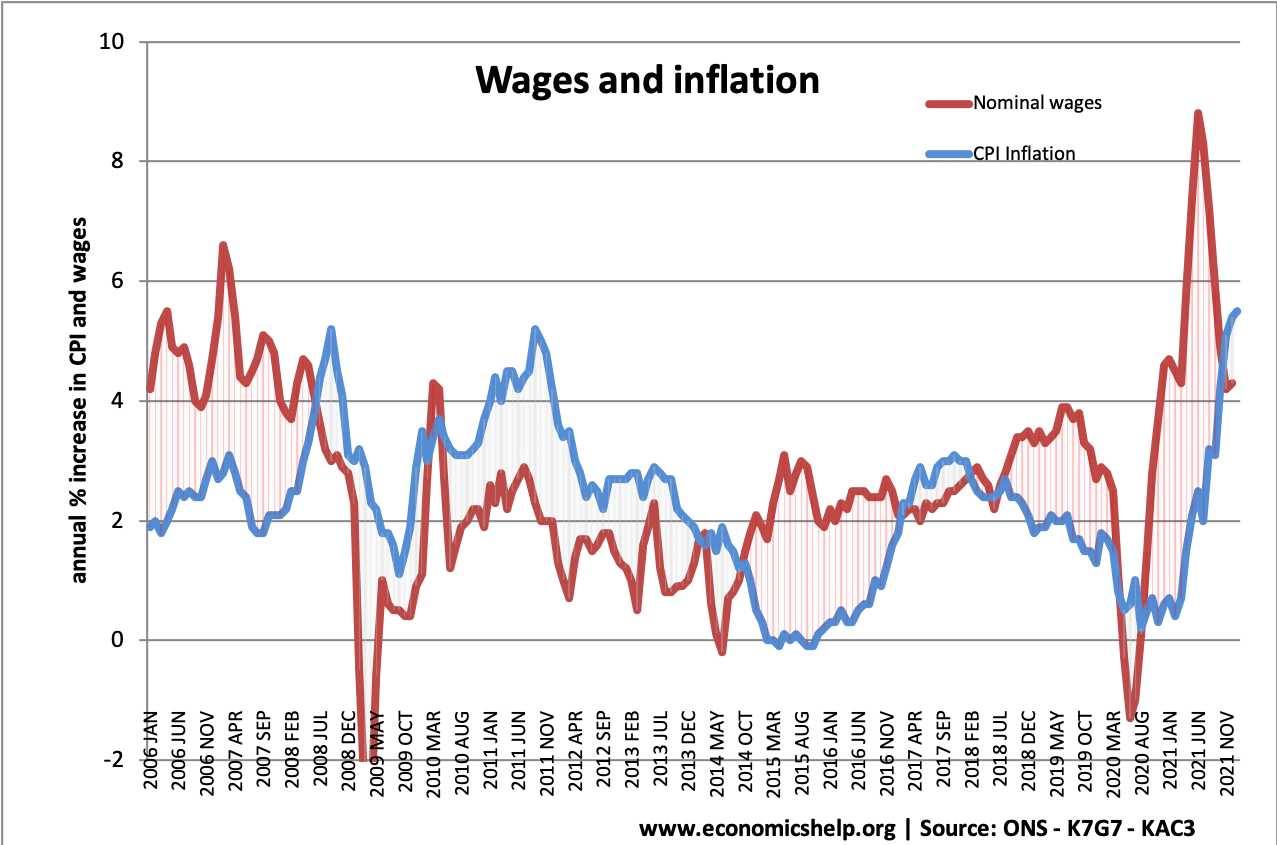
After the late 1980s inflation was brought under control, inflation remained for nearly two decades – during a period known as the great moderation. However since 2008 we have seen periods of cost-push inflation, most notably in 2022, with inflation rising close to 10% due to rising oil, gas and food prices.
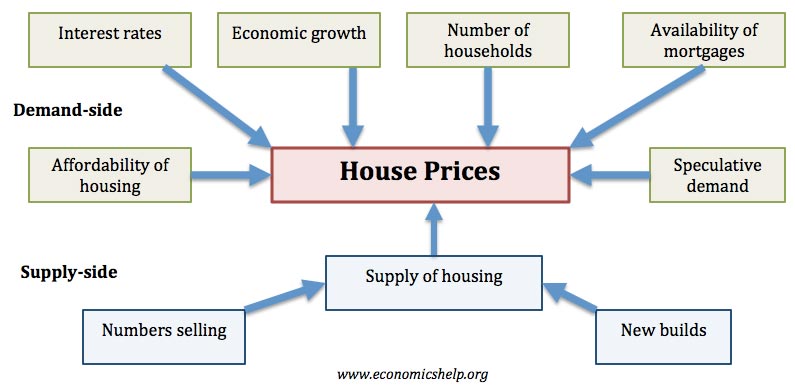
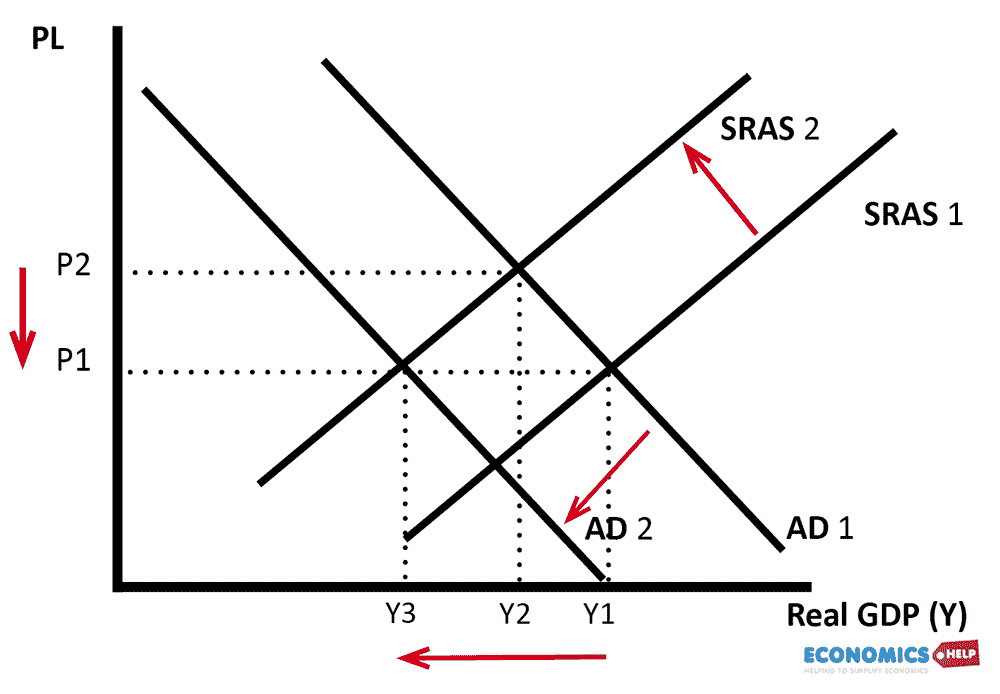
Inflation means an increase in the general price level and has the effect of reducing the value of money. Rising prices mean money buys less than it used to. See: Definition of Inflation
Inflation since 1860
Inflation 1949-2015