A quick look at benefit spending in the UK. This is a follow up to Social security spending. Thanks to HM Treasury for help in finding useful data set.
Source: Public Expenditure Statistical Analysis 2014 | Data Chapter 5 – 5.2
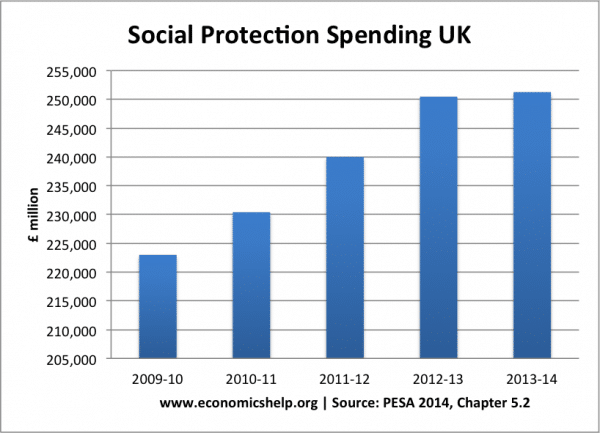
Social Protection spending
Firstly, there has been a modification to the category of government spending, now labelled – ‘Social protection spending’ – See: Social protection spending. This is not just welfare benefits. It includes personal social services, e.g paying for nursing, care in the community; (spending which could perhaps be better included with health care).
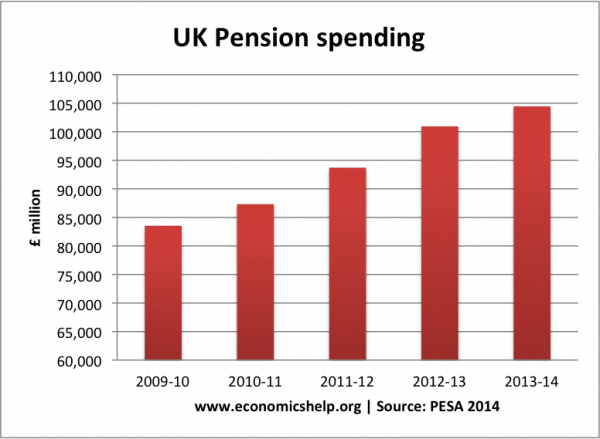
Secondly, by far the biggest level of social protection spending is pension spending. This includes both state pension payments and (I believe) state occupational pensions to retired public sector workers.
It is a very unwieldy sub-division of government spending, but if we look at whole budget it increased significantly during the great recession 2009-2013. This is partly due to the cyclical higher welfare payments expected during a period of unemployment and low income growth.
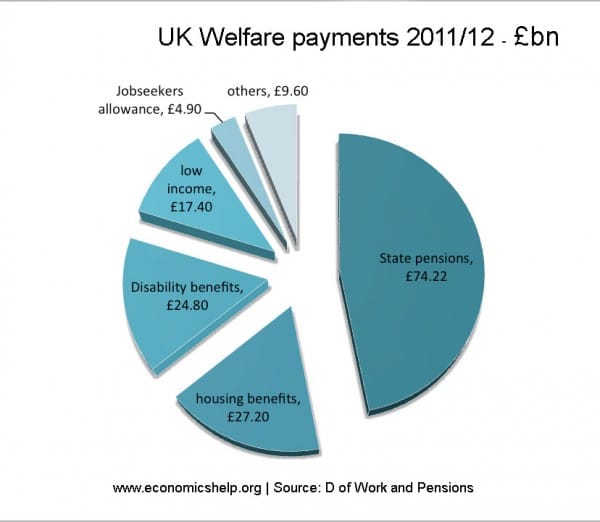
However, on closer examination, by far the biggest increase in spending from the social security budget is from pensions. Pension spending increased from £83bn in 2009/10 to £104.4 bn in 2013/14. An increase of £21 bn. In a period of so called austerity, that is a big increase in government spending.
- Unemployment benefit payments fell in this period from £5.5 bn to £4.9 bn
- Sickness and disability benefits rose from £30.6 bn to £37.5 bn
- Income support, tax credit (both family and social exclusion) declined from (£45.8bn) to £ 43.9 bn)
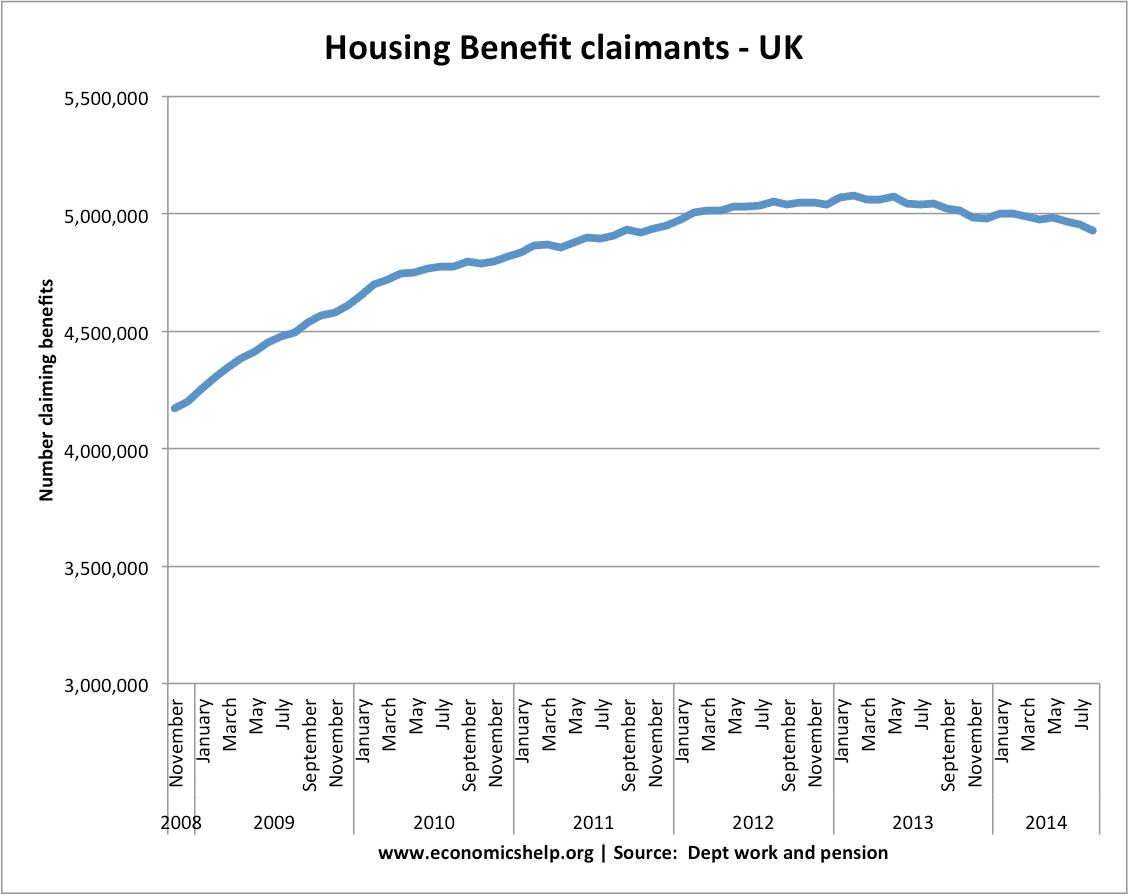
- Housing benefit from £22bn to £26bn (see: more on Housing benefit)
UK Pension spending