Externalities – Definition
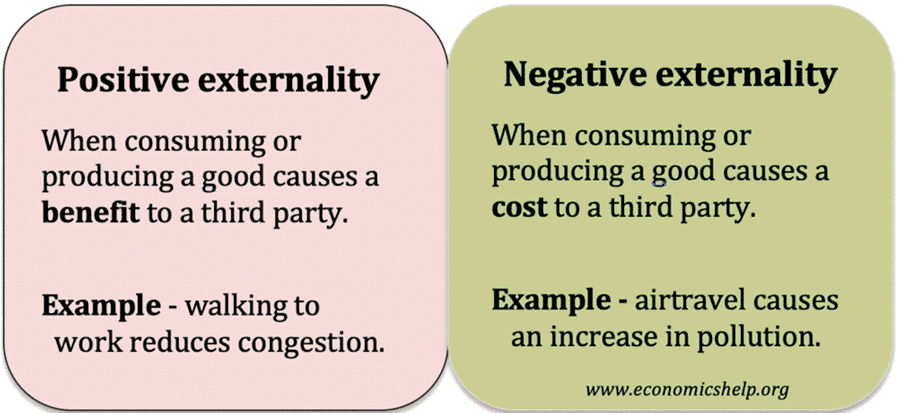
Externalities occur when producing or consuming a good cause an impact on third parties not directly related to the transaction. Externalities can either be positive or negative. They can also occur from production or consumption. For example, just driving into a city centre, will cause external costs of more pollution and congestion to those living …