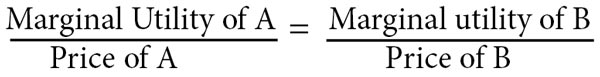Equimarginal principle
The equimarginal principle states that consumers will choose a combination of goods to maximise their total utility. This will occur where The consumer will consider both the marginal utility MU of goods and the price. In effect, the consumer is evaluating the MU/price. This is known as the marginal utility of expenditure on each item …