Carbon Tax- Advantages and Disadvantages
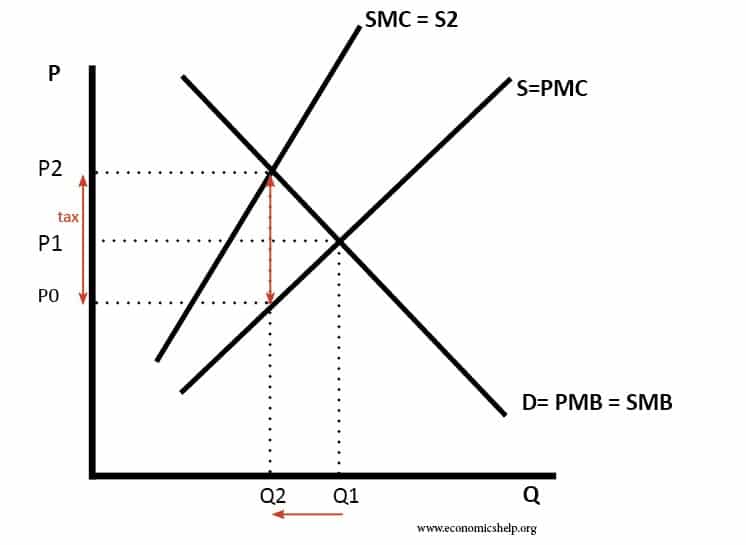
A Carbon tax is a specific tax on the consumption of goods which cause carbon dioxide emissions. C02 emissions have been identified as a major source of global warming and therefore, governments have been keen to reduce carbon emissions. Advantages of Carbon Taxes The market price is P1 – but this ignores the external cost …