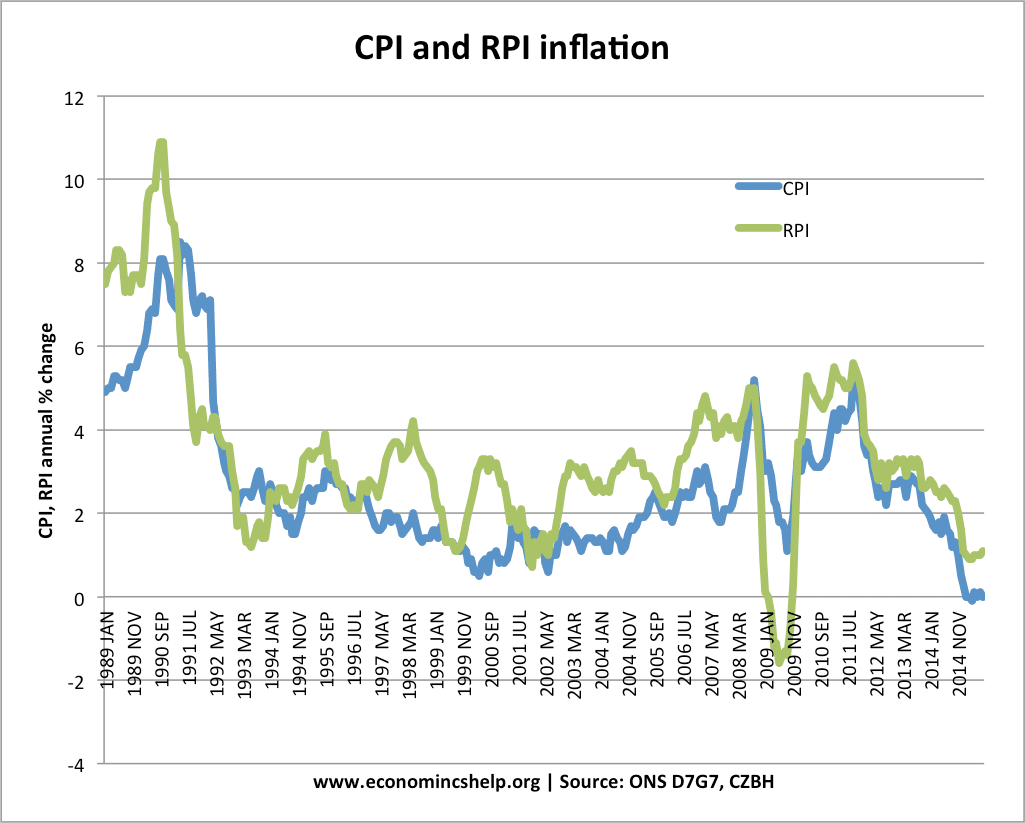
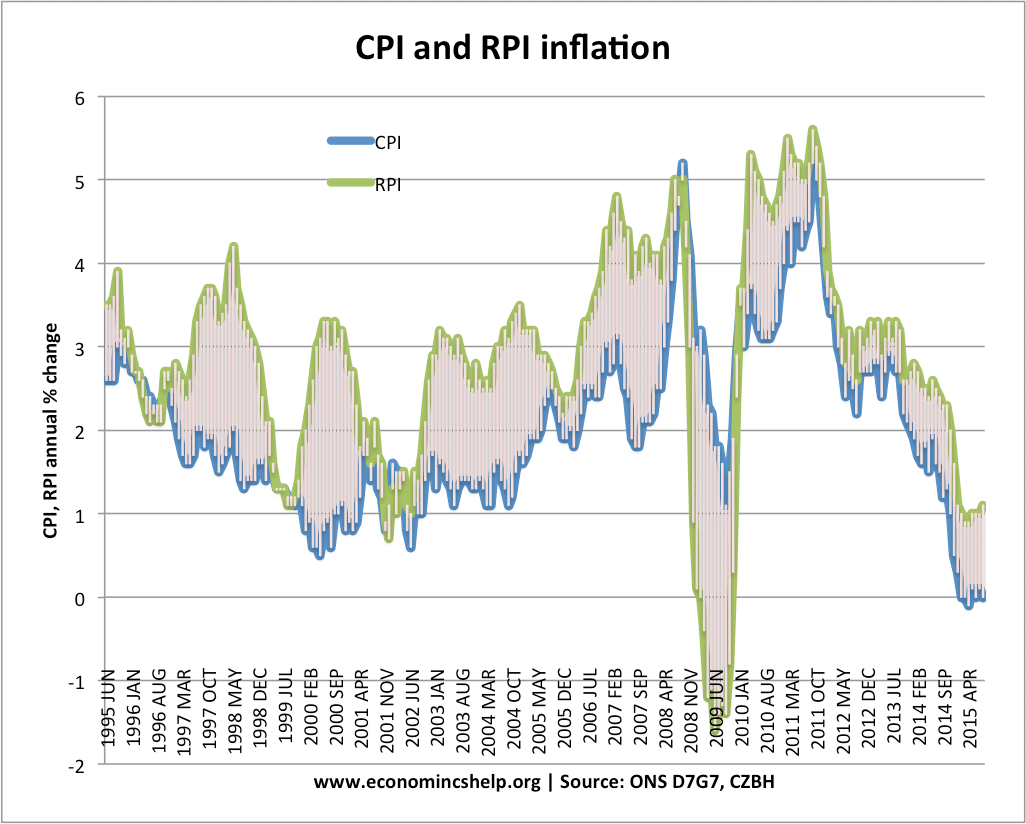
RPI, CPI and RPIX are three different measures for calculating inflation. To summarise
- CPI = headline rate (excludes mortgage interest payments, housing costs)
- RPI = Retail Price Index. Includes mortgage payments.
Source: ONS
In 2009, the UK saw a cut in interest rates, and therefore, a fall in mortgage repayments. This caused RPI to become negative – whilst CPI remained positive.
The main inflation rate in the UK is now the CPI Consumer Price Index.
The CPI is based on the HCIP (Harmonised Consumer index prices) which measures inflation on internationally agreed standards throughout Europe.
- The RPI (Retail price index) includes mortgage interest payments. Thus changes in the interest rates affect the RPI. If interest rates are cut, it will reduce mortgage interest payments. Thus the RPI will fall but not the CPI.
- The RPI also includes council tax and some other housing costs not included in CPI
- The CPI includes some financial services not included in the RPI
- The CPI is based on a wider sample of the population for working out weights.
RPIX and RPI
- RPIX is the same as RPI minus mortgage interest payments.
- RPIX is closer to CPI but not exactly same.
RPIY (Core Inflation)
The RPIY measures core inflation this is RPIX minus taxes such as VAT and excise duty. Thus a cut in VAT would reduce RPI but not reduce core RPIY
Which is Most Accurate Definition of Inflation?
RPI is generally higher – especially in periods of interest rate rises.
It’s hard to say. However, I think it is more useful to look at underlying core inflation. For example, a large cut in interest rates causes a temporary fall in RPI, yet could lead to inflationary pressures in the long term.
- CPI tends to be a little lower than RPI (except when interest rates are cut like at moment)
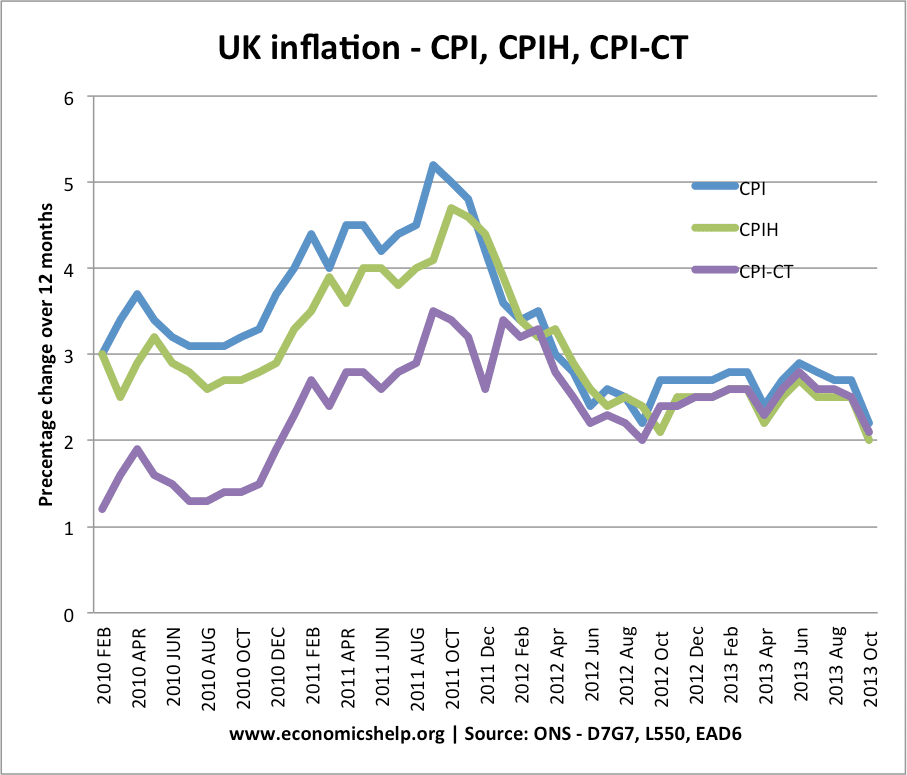
New measures of inflation – CPI, CPIH and CPIY
CPIH – CPIH It is based on CPI, plus it includes housing costs, such as mortgage interest payments. Owner occupiers cost (OOH) account for 12% of the CPIH weighting
CPIY – The CPI – Indirect taxes. This is the CPI measure but excludes the impact of indirect taxes such as VAT and excise duty.
CPI-CT. This is a similar principle to CPIY. CPI-CT holds indirect taxes rates constant at the rate prevailing at the start of the year.
See also notes on CPIY (basically CPI – indirect taxes)
- Definition inflation
- CPI and Core CPI
- RPI CPI at statistics.gov.uk
- Problems measuring inflation

Comments are closed.