To overcome market failure, the government can use various policies. For example, to reduce consumption of demerit goods, they can increase taxes.
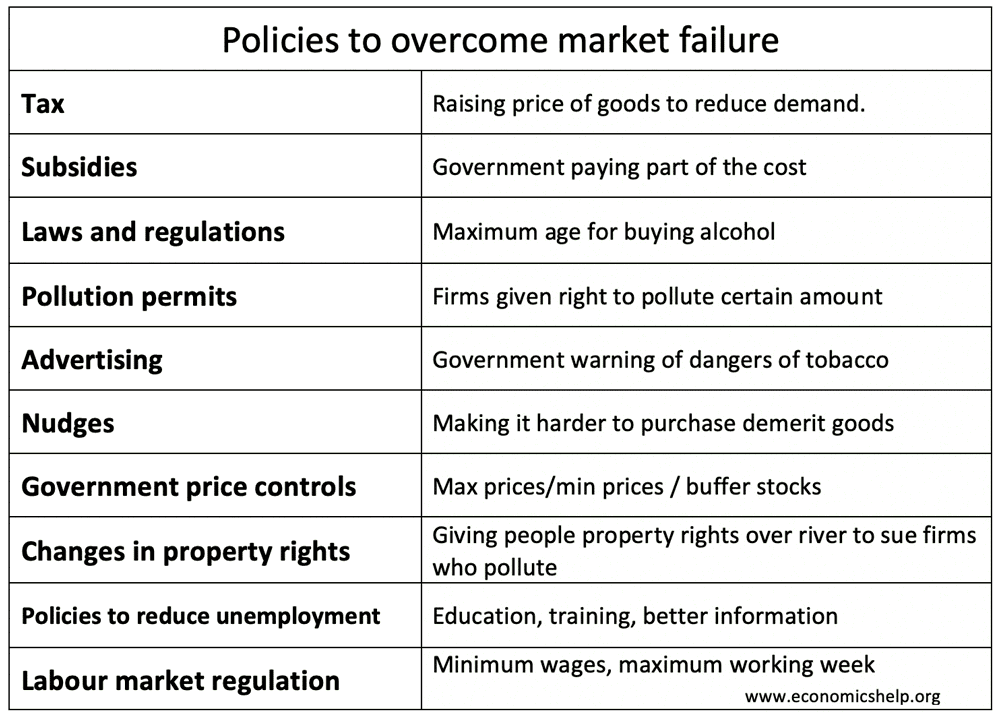
Policies to overcome market failure
- Taxes on negative externalities
- Subsidies on positive externalities
- Laws and Regulations
- Electronic Road Pricing – a specific tax related to congestion
- Pollution Permits – giving firms the ability to trade pollution permits.
- Advertising: Government campaigns to change people’s preferences.
- Nudges – use of behavioural economics
- Government price controls – Max and min prices Buffer stock schemes – Government price control to try to stabilise prices.
- Changes in Property Rights – Coase theorem
- Policies to overcome poverty/inequality – inequality can be seen as type of market failure
- Policies to reduce unemployment – policies to overcome market failures, such as geographical and occupational immobilities.
- Labour market regulation – Minimum wages to deal with monopsony power
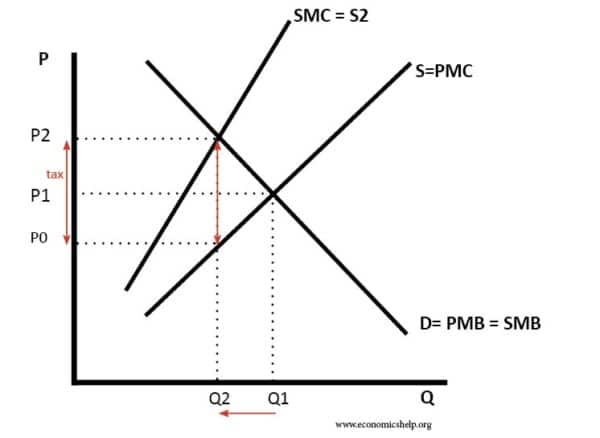
Tax
A tax shifts supply to the left and raises the price of the good.
Types of taxes to overcome market failure
- Airline tax
- Carbon Tax
- Cigarette Tax
- Death Tax
- Fat Tax
- Income tax
- Petrol tax
- Plastic bag
- Poll Tax
- Rubbish tax
- Tobin Tax
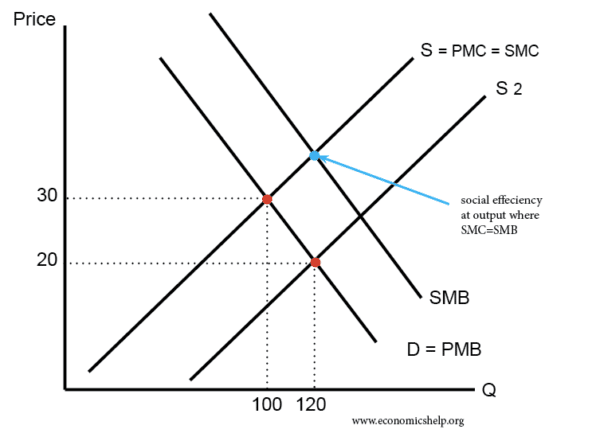
Subsidies
Subsidy shifts supply to the right and moves the equilibrium closer to where SMB = SMC.
- Farming subsidies – is there a case for extra subsidies for farmers?
- Subsidies for positive externalities
Government price controls
Labour market regulations
Related
- Government failure – when government efforts to reduce market failure lead to an inefficient outcome.